1 citations,
June 2016 in “FEBS open bio” Fish oil increased cell growth and macrophages in the skin but didn't affect COX-2 expression.
 April 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
April 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Sweat gland development involves two unique skin cell programs and a temporary skin environment.
 10 citations,
September 1997 in “Molecular carcinogenesis”
10 citations,
September 1997 in “Molecular carcinogenesis” Mirex seems to promote a unique group of skin cells different from those affected by another tumor promoter, TPA.
65 citations,
August 2013 in “Acta Biomaterialia” The new matrix improves skin regeneration and graft performance.
 26 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
26 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Researchers created early-stage hair-like structures from skin cells, showing how these cells can self-organize, but more is needed for complete hair growth.
 4 citations,
January 2013 in “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology”
4 citations,
January 2013 in “Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology” Certain transcription factors are key in controlling skin stem cell behavior and could impact future treatments for skin repair and hair loss.
 February 2024 in “Frontiers in physiology”
February 2024 in “Frontiers in physiology” Hair follicle stem cells help skin heal and grow during stretching.
 65 citations,
June 2003 in “EMBO journal”
65 citations,
June 2003 in “EMBO journal” Noggin overexpression delays eyelid opening by affecting cell death and skin cell development.
29 citations,
June 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Notch signaling disruptions can cause various skin diseases.
 13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology”
13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology” Melanoma development can be linked to the breakdown of skin's melanin-producing units.
 August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
August 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Human skin xenografting could improve our understanding of skin development, renewal, and healing.
 129 citations,
May 2015 in “Cell Stem Cell”
129 citations,
May 2015 in “Cell Stem Cell” Different types of stem cells exist within individual skin layers, and they can adapt to damage, transplantation, or tumor growth. These cells are regulated by their environment and genetic factors. Tumor growth is driven by expanding, genetically altered cells, not long-lived mutant stem cells. There's evidence of cancer stem cells in skin tumors. Other cells, bacteria, and genetic factors help maintain balance and contribute to disease progression. A method for growing mini organs from single cells has been developed.
 23 citations,
December 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
23 citations,
December 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Gene network oscillations inside hair stem cells are key for hair growth regulation and could help treat hair loss.
 November 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks”
November 2013 in “Elsevier eBooks” Skin and hair renewal is maintained by both fast and slow cycling stem cells, with hair regrowth primarily driven by specific stem cells in the hair follicle bulge. These cells can also help heal wounds and potentially treat hair loss.
52 citations,
February 2012 in “PloS one” Lack of Ctip2 in skin cells delays wound healing and disrupts hair follicle stem cell markers in mice.
10 citations,
June 2021 in “EMBO reports” When skin blisters, healing the wound is more important than growing hair, and certain stem cells mainly fix the blisters without helping hair growth.
 1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking a specific enzyme can reduce the negative impact of stress hormones on hair growth cells.
 114 citations,
April 2004 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
114 citations,
April 2004 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation causes dark skin patches and needs personalized treatment.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Finasteride helps female-pattern hair loss.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The study found that sweat glands normally suppress immune responses, but this is disrupted in certain skin diseases, possibly contributing to their development.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers created human cells that can turn into sebocytes, which may help study and treat skin conditions like acne.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Certain miRNAs might be involved in a hair loss condition called frontal fibrosing alopecia and could possibly help in its diagnosis.
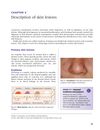
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
122 citations,
April 2020 in “American Journal Of Pathology” Skin aging is a complex process influenced by various factors, leading to wrinkles and sagging, and should be considered a disease due to its health impacts.
 508 citations,
February 2007 in “Cell”
508 citations,
February 2007 in “Cell” Epithelial stem cells are crucial for tissue renewal and repair, and understanding them could improve treatments for damage and cancer.
 May 2023 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” The document concludes that using stem cells to regenerate hair follicles could be a promising treatment for hair loss, but there are still challenges to overcome before it can be used clinically.
 3 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology”
3 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in cell and developmental biology” Melanocytes are important for skin and hair color and protect the skin from UV damage.
 April 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
April 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Skin healing from blisters can delay hair growth as stem cells focus on repairing skin over developing hair.
 22 citations,
September 2018 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
22 citations,
September 2018 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Facial aging is caused by natural processes and external factors, and can be managed with preventative measures and a variety of treatments tailored to individual needs.
 4 citations,
June 2021 in “Dermatology”
4 citations,
June 2021 in “Dermatology” Scientists created a 3D skin model to study a chronic skin disease and test treatments.























