 2 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” People with hair loss conditions may also have thyroid disorders, but more research is needed to understand the connection.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
 December 2015 in “Вестник дерматологии и венерологии”
December 2015 in “Вестник дерматологии и венерологии” Men with male pattern baldness may not have different hormone levels, but their hair follicles are likely more sensitive to hormones.

Nanocarriers with plant extracts show promise for safe and effective hair growth treatment.
 34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Some treatments work for common baldness, but there's less evidence for other hair loss types, and more research is needed.
 February 2024 in “Biomedicines”
February 2024 in “Biomedicines” Hormones like androgens, estrogen, thyroid hormones, and stress hormones can contribute to hair loss, and treatments target these hormonal imbalances.
 January 2024 in “Biomedicines”
January 2024 in “Biomedicines” Using stem cells from hair follicles to treat female hair loss is safe and effective after six months.
 February 2024 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual”
February 2024 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” NMN could potentially treat hair loss by reducing oxidative stress and improving cell health.
 October 1890 in “Science”
October 1890 in “Science” Pilocarpin can cause hair regrowth and color change in some cases but not in others, and it may have side effects in animals.
 June 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences”
June 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Adenosine complex helps increase hair thickness and density in hair loss.
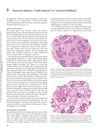 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Senescent alopecia is a type of hair loss that occurs after age 50, not caused by genetics, and involves a gradual thinning of hair without significant inflammation.
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” SVF injections improve hair growth and reduce hair loss in people with androgenic alopecia.
 September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
September 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Topical cetirizine may help increase hair length in male pattern baldness and could be an alternative to minoxidil with fewer side effects.
 28 citations,
March 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
28 citations,
March 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” There is no significant link between male pattern baldness and insulin resistance.
 20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
20 citations,
August 2005 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The protein ARA70/ELE1 is involved in male pattern baldness, and lower levels of its short form may lead to hair thinning.
 15 citations,
October 2017 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
15 citations,
October 2017 in “Dermatologic Clinics” New treatments for male hair loss show promise but need more research for safety and effectiveness.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps tell apart other hair loss conditions from common hair loss.
 5 citations,
September 1994 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology”
5 citations,
September 1994 in “The Journal of Dermatologic Surgery and Oncology” Scalp lifting surgery can safely and effectively reduce baldness if done with careful planning and proper technique.
 226 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
226 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair loss in women is genetic, diagnosed by examination and biopsy, and treated with minoxidil, finasteride, or transplantation.
 April 2019 in “Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research”
April 2019 in “Journal of emerging technologies and innovative research” Early treatment of Female Pattern Hair Loss is important to stop it from getting worse, and various treatments can help, especially in mild to moderate cases.

Male androgenetic alopecia (MAA) is a common, hereditary hair loss condition in men, linked to heart disease, and can be treated with minoxidil, finasteride, or hair transplantation.
 September 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
September 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy effectively diagnoses and assesses the severity of androgenetic alopecia.

Men with hair loss are seen as less attractive and shorter, and height is a key factor in attractiveness ratings.
 4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Actual harvested hair follicles were fewer and differed in type from estimated, with older patients and those with multiple transplants needing more careful planning.
 June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology”
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology” High-resolution MRI can distinguish between tertiary androgenetic alopecia and severe alopecia areata by measuring scalp and tissue thickness and hair follicle depth.
 February 2012 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism”
February 2012 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism” The document suggests more research is needed to understand the link between baldness and prostate cancer.
 57 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
57 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Platelet-rich plasma treatment can significantly increase hair count and density in men with pattern baldness, and these improvements can last up to 3 months.
2 citations,
December 2021 in “Cureus” Low vitamin D levels are linked to hair loss, and vitamin D might help treat it.
July 2020 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Young men with early hair loss and high SAA3 levels are at higher risk for heart disease.
 23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology”
23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology” Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, is likely an autoimmune disease with a genetic link, but its exact cause is still unknown.



























