 August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Infant skin cells may be less capable of repairing UV-induced DNA damage than adult cells.
 November 1966 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
November 1966 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The meeting discussed various skin conditions, treatments, and unusual cases, highlighting the effectiveness of tetracycline in treating rosacea.
1 citations,
March 2022 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Aging reduces skin stem cell function, leading to changes like hair loss and slower wound healing.
 January 2012 in “Else Kröner-Fresenius Symposia”
January 2012 in “Else Kröner-Fresenius Symposia” Maintaining DNA integrity in stem cells is crucial to prevent aging and cancer.
 August 2024 in “Cosmetics”
August 2024 in “Cosmetics” Caffeine is beneficial for skin and hair treatments but needs better delivery methods to penetrate deeper skin layers.
 19 citations,
March 1990 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology”
19 citations,
March 1990 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology” Minoxidil affects rat fluid dynamics, altering pressure and circulation, improving blood flow and hair growth.
 36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials”
36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials” A new skin-whitening agent using a peptide from wheat is safe and effective at reducing skin pigmentation.
 April 2024 in “Lasers in medical science”
April 2024 in “Lasers in medical science” Near-infrared LED light improves skin rejuvenation and hair growth better than white LED light.
 10 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of skin cancer”
10 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of skin cancer” PKC ε increases hair follicle stem cell turnover and may raise skin cancer risk.
 2 citations,
March 2014 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
2 citations,
March 2014 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The editor suggests removing "race" and "ethnicity" from dermatology and creating tools to objectively assess skin color and hair texture.
 October 2012 in “Humana Press eBooks”
October 2012 in “Humana Press eBooks” Grape seed extract is good for skin care, with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer effects.
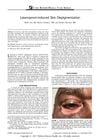 9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma”
9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma” Latanoprost eye drops may cause skin depigmentation.
 December 2019 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
December 2019 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Redheaded people have higher levels of a vitamin D precursor, suggesting red hair may be an adaptation for better vitamin D synthesis in areas with less sunlight.
 101 citations,
October 2016 in “Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine”
101 citations,
October 2016 in “Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine” Fullerenes show potential in skin care but need more safety research.
 6 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Environmental stressors like UV radiation, pollution, and extreme temperatures can damage skin and lead to diseases and aging.
 70 citations,
March 2008 in “Mechanisms of Ageing and Development”
70 citations,
March 2008 in “Mechanisms of Ageing and Development” Maintaining DNA health in stem cells is key to preventing aging and tissue breakdown.
 75 citations,
January 2014 in “Archiv Der Pharmazie”
75 citations,
January 2014 in “Archiv Der Pharmazie” Jasmonic acid and its derivatives play important roles in plant health and have potential uses in medicine and agriculture.
 November 2024 in “Nanomaterials”
November 2024 in “Nanomaterials” The nanocrystalline suspension effectively delivers dutasteride over time with minimal inflammation.
 4 citations,
May 2020 in “Medicine in Drug Discovery”
4 citations,
May 2020 in “Medicine in Drug Discovery” The study developed a method to detect minoxidil and its sulfate form, found that minoxidil sulfate is temperature-sensitive, and identified a way to potentially increase its stability for hair loss treatment.
 September 2022 in “Intisasi sains media”
September 2022 in “Intisasi sains media” A young child with complete hair loss improved significantly with a combination of hair growth treatments and laser therapy.
5 citations,
July 2022 in “Genes” Increasing EGR1 levels makes hair root cells grow faster.
 11 citations,
July 2021 in “Physiologia Plantarum”
11 citations,
July 2021 in “Physiologia Plantarum” SIPHL1 from tomato enhances plants' response to low phosphate levels.
 520 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS biophysics”
520 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS biophysics” Photobiomodulation therapy using red and near-infrared light can reduce inflammation and aid in healing various conditions.
 41 citations,
September 2017 in “Advanced Healthcare Materials”
41 citations,
September 2017 in “Advanced Healthcare Materials” A special hydrogel helps heal skin without scars and regrows hair.
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Photochemical & photobiological sciences” Grasp protein helps maintain skin health after UVB exposure.
 7 citations,
June 2021 in “Cell Proliferation”
7 citations,
June 2021 in “Cell Proliferation” Low oxygen levels improve the function of hair and skin cells when they are in direct contact.
 5 citations,
June 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Putting thymidine dinucleotide on newborn mice's skin can delay and reduce skin cancer.
 36 citations,
November 2018 in “BMC plant biology”
36 citations,
November 2018 in “BMC plant biology” ROXY proteins help plants respond to nitrate shortage by affecting nutrient sensing and growth.
 4 citations,
January 2022 in “Yonsei Medical Journal”
4 citations,
January 2022 in “Yonsei Medical Journal” Microneedles are a promising method for drug delivery, offering efficient and convenient alternatives with fewer side effects.
 20 citations,
April 2014 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
20 citations,
April 2014 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Sulfotransferase in hair follicles helps predict how well minoxidil works for female hair loss.



























