 77 citations,
March 2021 in “Nature”
77 citations,
March 2021 in “Nature” Stress hormone corticosterone blocks a growth factor to slow down hair stem cell activity and hair growth.
 August 2021 in “Journal of Fundamental and Applied Pharmaceutical Science”
August 2021 in “Journal of Fundamental and Applied Pharmaceutical Science” Black tea extract at 5% concentration promotes the most hair growth.
 August 2024 in “Indian Journal Of Clinical Practice”
August 2024 in “Indian Journal Of Clinical Practice” A balanced diet and healthy lifestyle help manage PCOS symptoms.
 14 citations,
June 2018 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
14 citations,
June 2018 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Green tea compound EGCG helps mink hair follicles grow by affecting certain cell growth pathways.
 3 citations,
July 2013 in “Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry”
3 citations,
July 2013 in “Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry” Chinese black tea extract helped mice grow hair, especially when combined with capsaicin.
 22 citations,
March 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
22 citations,
March 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” New acne treatments show promise as alternatives to traditional therapies.
 5 citations,
January 2013 in “PubMed”
5 citations,
January 2013 in “PubMed” Green tea may help with various skin conditions and protect the skin when taken orally or applied topically, but its effectiveness is not always proven.
 4 citations,
March 2012 in “Annals of oncology”
4 citations,
March 2012 in “Annals of oncology” New treatment with green tea polyphenols and nicotinamide improves skin problems from cancer therapy.
July 2011 in “Hair transplant forum international” No clear evidence links green tea to hair loss through iron deficiency.
 3 citations,
June 2009 in “The journal of alternative and complementary medicine/Journal of alternative and complementary medicine”
3 citations,
June 2009 in “The journal of alternative and complementary medicine/Journal of alternative and complementary medicine” Green tea extract may help reduce excessive hair growth.

Green tea extract helped heal rabbit skin burns better than antibiotic ointment.
 December 2022 in “Korean journal of medicinal crop science/Han-gug yagyong jagmul hag-hoeji”
December 2022 in “Korean journal of medicinal crop science/Han-gug yagyong jagmul hag-hoeji” Natural extracts like ginseng, green tea, shiitake, and aloe vera may help prevent hair loss by protecting hair-related cells.
 6 citations,
May 2009 in “Cell transplantation”
6 citations,
May 2009 in “Cell transplantation” Green tea component EGCG helps keep rat skin grafts viable longer.
Low-temperature extracts of black beans, peony, and green tea improve scalp health and are better than traditional hot-water extracts.
 1 citations,
November 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” The new anti-dandruff shampoo with ketoconazole-coated zinc oxide nanoparticles is more effective against dandruff.
90 citations,
July 2009 in “PTR. Phytotherapy research/Phytotherapy research” Spearmint tea may reduce testosterone and self-reported hair growth in women with PCOS.
 January 2024 in “Brazilian Journal of Hair Health”
January 2024 in “Brazilian Journal of Hair Health” Some plant-based products might treat hair loss with fewer side effects than current medications.
The document does not provide the results or effectiveness of the green tea and gotukola extract hair growth treatment.

Drinking sweetened tea and late bedtimes increase the risk of hair loss in women.
December 2015 in “아시안뷰티화장품학술지” Green tea's EGCG has various health benefits, including antioxidant properties, skin protection, cancer cell growth inhibition, anti-inflammatory effects, fat breakdown, detoxification, diabetes management, hair growth stimulation, and prevention of gum disease.
 20 citations,
February 2013 in “Nutrition”
20 citations,
February 2013 in “Nutrition” Selenium-enriched green tea might be a safe prebiotic for gut health.
September 2022 in “The Korean Tea Society” Houttuynia cordata compounds may help with anti-aging and hair loss.
 2 citations,
November 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
2 citations,
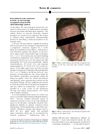
November 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Drinking kava tea can cause a skin reaction with red, swollen bumps, which may improve with steroids.
 2 citations,
September 2018 in “Tissue Engineering Part A”
2 citations,
September 2018 in “Tissue Engineering Part A” Xeno-free three-dimensional stem cell masses are safe and effective for improving blood flow and tissue repair in limb ischemia.
August 2022 in “Tissue Engineering Part A” Advancements in skin treatment and wound healing include promising gene therapy, 3D skin models, and potential new therapies.
 46 citations,
September 2014 in “Tissue engineering. Part A”
46 citations,
September 2014 in “Tissue engineering. Part A” Researchers created hair-inducing human cell clusters using a 3D culture method.
27 citations,
January 2017 in “Journal of clinical and diagnostic research” A woman poisoned with thallium was successfully treated with activated charcoal and Prussian blue.
 4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis”
4 citations,
February 2022 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis” The conclusion is that a new method can measure caffeine and drugs in hair, finding caffeine abusers have 70 times more caffeine than normal, with a proposed cut-off value for abuse.
 May 2023 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2023 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Various substances, including cosmetic sponges, vein glue, chai tea, skincare products, and medicaments, can cause allergic contact dermatitis, and healthcare workers often react to N95 masks.
1 citations,
February 2017 in “PubMed” The supplement may help hair growth and is safe, but more research is needed.





















