1 citations,
March 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Radiation therapy damages skin structure and immune function, causing inflammation and potential hair loss.
 May 2024 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
May 2024 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” A man with a type of skin lymphoma had unusual yellowish skin growths despite normal blood lipid levels, and treatment reduced some symptoms but not the growths.
[object Object] March 2024 in “Veterinary sciences” Geriatric Julia Creek dunnarts often suffer from reproductive and skin diseases, impacting conservation efforts.
 23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology”
23 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in dermatology” Alopecia areata involves immune response and gene changes affecting hair loss.
 34 citations,
October 2011 in “Pathology Research International”
34 citations,
October 2011 in “Pathology Research International” Behçet's Disease may be caused by genetic and environmental factors leading to abnormal immune responses, and stress management and new treatments could improve patient outcomes.
 16 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of Medical Primatology”
16 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of Medical Primatology” The monkey's hair loss was due to an autoimmune disease, not genetics.
 24 citations,
November 1992 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
24 citations,
November 1992 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Early diagnosis and aggressive treatment are crucial for better outcomes in lymphomatoid granulomatosis.
 January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus has different forms, is influenced by genetic and environmental factors, and can be treated with various medications, but more targeted therapies are needed.
 June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” ILC1-like cells can cause alopecia areata by attacking hair follicles.
328 citations,
November 2020 in “Nature Materials” Hydrogel scaffolds can help wounds heal better and grow hair.
 January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Pediatric alopecia areata is more immune-active than adult cases, suggesting age-specific treatments and potential use of JAK inhibitors.
 29 citations,
January 2007 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
29 citations,
January 2007 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Eyebrow loss has many causes and requires accurate diagnosis for proper treatment.
4 citations,
October 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Using an anti-ICAM-1 antibody with rapamycin improves hair transplant survival in monkeys.
47 citations,
June 2013 in “Biology of blood and marrow transplantation” Mice with human fetal thymic tissue and stem cells developed symptoms similar to chronic graft-versus-host disease.
7 citations,
July 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Oral lichen planus is a chronic disease causing mouth discomfort and sometimes needs immunosuppressive treatment.
 19 citations,
March 1997 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
19 citations,
March 1997 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Alopecia areata involves specific T-cells, unlike androgenetic alopecia.
[object Object]  28 citations,
October 2019 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology”
28 citations,
October 2019 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology” Hair can regrow in large wounds through a process similar to how hair forms in embryos, and understanding this could lead to new treatments for hair loss or scarring.
 4 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
4 citations,
November 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” New treatments targeting T-cell pathways are needed for better alopecia areata management.
 1 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Possible link between hair loss and metabolic syndrome, with RANTES as a potential clue.
 33 citations,
July 1992 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
33 citations,
July 1992 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil doesn't affect perifollicular lymphoid infiltration in alopecia areata patients.
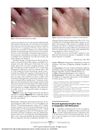 9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology”
9 citations,
May 2013 in “JAMA Dermatology” Sunlight exposure improved a patient's skin condition, and there may be a link between a certain disease and skin growths; a leukemia treatment caused changes in hair color and growth.
 November 2023 in “Klìtinna ta organna transplantologìâ”
November 2023 in “Klìtinna ta organna transplantologìâ” MSC-derived exosomes can help treat COVID-19, hair loss, skin aging, and arthritis.
 125 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Immunology”
125 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Immunology” Foxp3 is crucial for regulatory T cell function, and targeting these cells may help treat immune disorders.
 4 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
4 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” The dog with an Alopecia Areata-like condition showed signs of an autoimmune disease and partially regrew hair without treatment, suggesting dogs could be models for human AA research.
28 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine” VDC-1101 shows potential as a treatment for canine cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
 2 citations,
May 2019 in “Advances in wound care”
2 citations,
May 2019 in “Advances in wound care” Blood-derived CD34+ cells speed up healing, reduce scarring, and regrow hair in skin wounds.
 30 citations,
July 2019 in “PloS one”
30 citations,
July 2019 in “PloS one” Patients with Alopecia areata have fewer specific immune cells that normally regulate the immune system, which may contribute to the condition.
 18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
18 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Certain immune cells contribute to severe hair loss in chronic alopecia areata, with Th17 cells possibly having a bigger impact than cytotoxic T cells.
 January 2023 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
January 2023 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” A substance called miR-1246 may help treat severe hair loss by reducing certain immune cell activities.
 278 citations,
March 2013 in “Gut”
278 citations,
March 2013 in “Gut” Anti-IL-12/IL-23 antibody therapy effectively treats psoriasiform skin lesions in IBD patients.






















