 19 citations,
January 2007 in “Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin”
19 citations,
January 2007 in “Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin” Glycine reduces skin pigmentation by lowering melanin production.
 July 2021 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy”
July 2021 in “Journal of dermatology research and therapy” Using combined treatments can help manage acne by targeting the bacteria and skin changes that cause it.
 41 citations,
December 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Understanding how melanocyte stem cells work could lead to new treatments for hair graying and skin pigmentation disorders.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that a deeper understanding of skin aging and photodamage is needed to create better skin treatments.
 23 citations,
March 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
23 citations,
March 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” ATP increases melanin production in skin after UV exposure, with the P2X7 receptor being crucial for this process.
 1 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of Biomedical Optics”
1 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of Biomedical Optics” Reflectance spectroscopy can noninvasively track hair growth stages by measuring skin reflectance and melanin changes.
 23 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
23 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Microneedling is a safe and effective way to improve various skin conditions with minimal side effects.
8 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Modified phenol peels effectively reduced stubborn skin pigmentation in patients with Lichen Planus Pigmentosus.
September 2018 in “Obsgyne Review Journal of Obstetric and Gynecology of Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society” Pregnant women often experience a variety of skin problems, including pigmentation changes and stretch marks.
31 citations,
November 2015 in “PloS one” Reducing Tyrosinase prevents mature color pigment cells from forming in mouse hair.
 19 citations,
August 2020 in “Gastroenterology report”
19 citations,
August 2020 in “Gastroenterology report” There is no standard treatment for the rare Cronkhite–Canada syndrome, which can be fatal and lead to cancer.
 3 citations,
May 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin lesions in Carney Complex are caused by a gene change in some skin cells that leads to increased pigmentation and may lead to tumors.
 36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials”
36 citations,
March 2014 in “Biomaterials” A new skin-whitening agent using a peptide from wheat is safe and effective at reducing skin pigmentation.
29 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” P-cadherin is crucial for hair follicle pigmentation but not skin pigmentation.
96 citations,
August 1995 in “Bone” Vitamin D3 is important for bone health and may help treat various diseases beyond bone-related conditions.
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” Radiation therapy for cancer often causes skin problems like redness, dryness, and pain.
 December 2024 in “Nutrients”
December 2024 in “Nutrients” Skin, hair, and nail changes can help detect eating disorders early.
 6 citations,
February 2014 in “Human & experimental toxicology”
6 citations,
February 2014 in “Human & experimental toxicology” Testosterone injections can cause skin darkening and thickening.
 38 citations,
June 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
38 citations,
June 2017 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Aging in hair follicle stem cells leads to hair graying, thinning, and loss.
 77 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
77 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Environmental factors, hormones, nutrition, and stress all significantly affect skin health and aging.
 4 citations,
October 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Dermoscopy shows that diffuse alopecia areata progresses through specific hair growth stages.
 33 citations,
September 2016 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
33 citations,
September 2016 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Fractional resurfacing is safe and effective for certain skin conditions in Asian patients, but care must be taken to avoid skin pigmentation issues.
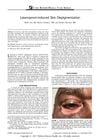 9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma”
9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma” Latanoprost eye drops may cause skin depigmentation.
8 citations,
January 2010 in “Springer eBooks” Plastic surgeons need to understand skin anatomy and physiology to effectively treat aging and diverse skin types.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Advances in stem cells and their niches”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Advances in stem cells and their niches” Dermal papilla cells are key for hair growth and color, influencing hair type and size, and their interaction with stem cells could help treat hair loss and color disorders.
 20 citations,
September 2020 in “International journal of computer applications”
20 citations,
September 2020 in “International journal of computer applications” The Random Forest algorithm was the most accurate at diagnosing Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome.
 187 citations,
December 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology”
187 citations,
December 2005 in “Experimental Dermatology” Estrogens can improve skin aging but carry risks; more research is needed on safer treatments.
 74 citations,
March 2001 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
74 citations,
March 2001 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that skin biopsies, genetic and environmental factors, and specific treatments are important in managing cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
 January 2024 in “Archives of pharmacy practice”
January 2024 in “Archives of pharmacy practice” The skin is vital for protection, temperature control, fluid balance, immunity, and sensing, with damage affecting daily life and mental health.























