 9 citations,
February 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
9 citations,
February 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Older mice have stiffer skin with less elasticity due to changes in collagen and skin structure, affecting aging and hair loss.
[object Object]  4 citations,
March 2017 in “Development”
4 citations,
March 2017 in “Development” Estrogen is important for keeping adult mouse nipple skin healthy by controlling certain cell signals.
 87 citations,
January 2016 in “Development”
87 citations,
January 2016 in “Development” Blocking β-catenin in skin cells improves hair growth during wound healing.
84 citations,
December 2008 in “Developmental biology” Retinoic acid-binding proteins in skin are regulated by β-catenin and Notch signalling.
 23 citations,
November 2018 in “Development, Growth & Differentiation”
23 citations,
November 2018 in “Development, Growth & Differentiation” Epidermal stem cells have various roles in skin beyond just maintenance, including forming specialized structures and aiding in skin repair and regeneration.
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of developmental biology” Bird foot scales develop differently and can repair but not fully regenerate due to the lack of specialized stem cell areas.
[object Object]  128 citations,
October 2011 in “Development”
128 citations,
October 2011 in “Development” Activating a protein called β-catenin in adult skin can make it behave like young skin, potentially helping with skin aging and hair loss.
 65 citations,
January 2018 in “Nature Reviews Endocrinology”
65 citations,
January 2018 in “Nature Reviews Endocrinology” Skin fat has important roles in hair growth, skin repair, immune defense, and aging, and could be targeted for skin and hair treatments.
3 citations,
February 2015 in “Mechanisms of development” Hormones and stretching both needed for nipple area skin growth in mice.
 28 citations,
July 2008 in “Developmental Biology”
28 citations,
July 2008 in “Developmental Biology” Smad4 is important for healthy hair follicles because it helps produce a protein needed for hair to stick together and grow.
22 citations,
December 2013 in “Stem cells and development” Horse skin stem cells combined with platelet-rich plasma improve skin healing.
 61 citations,
October 1996 in “Development”
61 citations,
October 1996 in “Development” Hair growth can be stimulated by combining certain skin cells, which can rejuvenate old cells and cause them to specialize in hair follicle creation.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The conclusion is that the cornea has two types of stem cells, with Lrig1+ cells being key for renewal in aging corneas, independent of CD44.
63 citations,
April 2005 in “Mechanisms of development” Mice with too much Claudin-6 have skin barrier problems and abnormal hair growth.
 19 citations,
November 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
November 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The spiny mouse can regenerate its skin without scarring, which could help us learn how to heal human skin better.
 610 citations,
April 2014 in “Nature Reviews Immunology”
610 citations,
April 2014 in “Nature Reviews Immunology” The document concludes that understanding how the skin's immune system and inflammation work is complex and requires more research to improve treatments for skin diseases.
 138 citations,
May 2000 in “Maturitas”
138 citations,
May 2000 in “Maturitas” Estrogen replacement can improve skin health in menopausal women but doesn't reverse sun damage or prevent hair loss.
 96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
96 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The document concludes that adult mammalian skin contains multiple stem cell populations with specific markers, important for understanding skin regeneration and related conditions.
 7 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
7 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Knowing how skin works and its diseases helps doctors diagnose and treat skin conditions better.
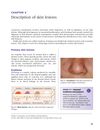
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 276 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
276 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The document concludes that mouse models are helpful but have limitations for skin wound healing research, and suggests using larger animals and genetically modified mice for better human application.
 211 citations,
October 2001 in “The FASEB Journal”
211 citations,
October 2001 in “The FASEB Journal” Noggin is necessary to start the hair growth phase in skin after birth.
 208 citations,
December 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
208 citations,
December 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Certain cells from hair follicles can create new hair and contribute to hair growth when implanted in mice.
 149 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
149 citations,
July 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” The dermal papilla is crucial for hair growth and health, and understanding it could lead to new hair loss treatments.
 133 citations,
September 2013 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
133 citations,
September 2013 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Different types of stem cells and their environments are key to skin repair and maintenance.
 127 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Biological Rhythms”
127 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Biological Rhythms” The skin's internal clock affects healing, cancer risk, aging, immunity, and hair growth, and disruptions can harm skin health.
 116 citations,
August 2010 in “Nature”
116 citations,
August 2010 in “Nature” Scientists turned rat thymus cells into stem cells that can help repair skin and hair.
 75 citations,
January 2011 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery”
75 citations,
January 2011 in “Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery” The dermal regeneration template is effective in skin regeneration, reducing scarring, and has potential for future improvements.
 46 citations,
December 2018 in “Genes & Development”
46 citations,
December 2018 in “Genes & Development” Lung repair involves both dedicated and flexible stem cells, important for developing new treatments.
 24 citations,
October 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
24 citations,
October 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Genetic research has advanced our understanding of skin diseases, but complex conditions require an integrative approach for deeper insight.

























