 45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” Topical immunotherapy, especially with DPCP, is effective for treating severe alopecia areata.
 30 citations,
April 1997 in “European journal of endocrinology”
30 citations,
April 1997 in “European journal of endocrinology” The document concludes that managing hirsutism involves identifying the cause, using a scoring system for severity, combining cosmetic and medical treatments, encouraging weight loss, and providing psychological support, while noting the need for more research on drug treatments.
 February 2023 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
February 2023 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Laser treatment, especially when combined with other therapies, is effective for hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
 January 2019 in “Clinical Dermatology Open Access Journal”
January 2019 in “Clinical Dermatology Open Access Journal” Combining corticosteroids and non-ablative fractional laser therapy may effectively treat extensive alopecia areata.
 85 citations,
June 2006 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
85 citations,
June 2006 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” The document concludes that hirsutism is the main sign for diagnosing hyperandrogenism, which requires a detailed patient history and physical exam.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Intralesional corticosteroids are the best for limited alopecia areata, oral steroids are less effective, and PRP is safe and promising, especially for children and severe cases.
 1 citations,
November 2017 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs”
1 citations,
November 2017 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs” Scientists now better understand the genetics of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, leading to more accurate diagnoses and potential new treatments.
31 citations,
September 2020 in “Clinical endocrinology” Some antiandrogens may lower testosterone better than others, but it's unclear which is best for feminization in transgender women; more research is needed.
 64 citations,
March 2017 in “Nature communications”
64 citations,
March 2017 in “Nature communications” Researchers found 63 genes linked to male-pattern baldness, which could help in understanding its biology and developing new treatments.
 10 citations,
September 2022 in “Advanced Healthcare Materials”
10 citations,
September 2022 in “Advanced Healthcare Materials” Current methods can't fully recreate skin and its features, and more research is needed for clinical use.
April 2024 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Alopecia areata and vitiligo share immune system dysfunction but differ in specific immune responses and affected areas.
 September 2022 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
September 2022 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Dermoscopy helped diagnose a rare skin disease which slightly improved with treatment.
 3 citations,
October 2019 in “Pharmaceutics”
3 citations,
October 2019 in “Pharmaceutics” New technique implants pigment in scalp with less pain and damage.
 16 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
16 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Alopecia areata has a complex genetic basis that was not fully understood as of 2001.
 13 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
13 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Clobetasol and pimecrolimus are similarly effective for alopecia areata, but pimecrolimus has fewer side effects and is preferred for long-term use.
 41 citations,
June 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders”
41 citations,
June 2016 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders” Hidradenitis suppurativa may be related to hormones and patients often have metabolic disorders; more research is needed to understand this connection.
 24 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
24 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Balding people may have higher heart disease risk.
 6 citations,
May 2015 in “Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice”
6 citations,
May 2015 in “Veterinary Clinics of North America: Equine Practice” Horse skin diseases are complex to manage and often require a biopsy for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 5 citations,
January 2001 in “Advances in protein chemistry”
5 citations,
January 2001 in “Advances in protein chemistry” 5α-reductase inhibitors help treat disorders caused by DHT and have potential for future therapies.
 3 citations,
September 2000 in “Geriatric nursing”
3 citations,
September 2000 in “Geriatric nursing” Aging men face unique health issues like erectile dysfunction, prostate problems, and baldness.
 71 citations,
January 2015 in “The Scientific World Journal”
71 citations,
January 2015 in “The Scientific World Journal” Insulin resistance may contribute to various skin diseases and treating it could improve skin health and prevent more serious conditions.
 48 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
48 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Skin problems are common and important signs of eating disorders and treating the eating disorder can improve these skin conditions.
 33 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
33 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Eating disorders can cause skin problems that need treating the underlying condition for better health.
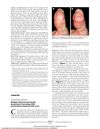 11 citations,
December 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology”
11 citations,
December 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology” A man with rare skin changes on his fingers was diagnosed with multiple myeloma-linked amyloidosis.
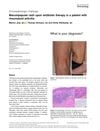 1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Methotrexate caused a rare skin rash in a rheumatoid arthritis patient, which resolved after stopping the drug.
 July 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document reviews key historical figures and discoveries in dermatology.
 September 2017 in “Majallah-i taḥqīqāt-i ̒ulūm-i pizishkī-i Zāhidān”
September 2017 in “Majallah-i taḥqīqāt-i ̒ulūm-i pizishkī-i Zāhidān” Androgenetic alopecia is a long-term, immune-related disorder that starts during puberty due to androgen secretion, and it might be improved with iron tablets, platelet transfusion, and anti-inflammation therapy.
26 citations,
June 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology clinics of North America” More research is needed to understand the long-term benefits of insulin-sensitizing drugs for treating adolescents with PCOS.
6 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata involves complex immune and genetic factors, with potential treatment targets identified, but more research is needed.
 June 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
June 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Both DPCP alone and with PRP are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata.


























