 1 citations,
June 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
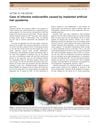
June 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A man got heart infection from scalp infection caused by artificial hair implants.
 3 citations,
March 2021 in “Cureus”
3 citations,
March 2021 in “Cureus” A rare combination of halo nevi, nonsegmental vitiligo, and early gray hair can occur together.
1 citations,
June 2018 in “Pharmaciana” The hair tonic with 15% ethanol effectively promotes hair growth.
 20 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
20 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Green tea may help with skin health and protect against UV damage, but more research is needed to confirm its safety and effectiveness.
 36 citations,
February 2004 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
36 citations,
February 2004 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Different sports can cause specific skin conditions that need proper diagnosis and treatment.
5 citations,
October 2020 in “Veterinary record case reports” Fluorescent light energy may help treat skin infections in dogs with calcinosis cutis.
 20 citations,
January 2018 in “Expert opinion on emerging drugs”
20 citations,
January 2018 in “Expert opinion on emerging drugs” JAK inhibitors may soon be a safe and effective treatment for alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
1 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” 0.05% Betamethasone Dipropionate is the most effective topical treatment for alopecia areata.
 14 citations,
January 2015 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Acitretin significantly reduced inflammatory attacks in a woman with Naevus Comedonicus Syndrome but caused side effects.

Early diagnosis and lifelong zinc supplementation are crucial for treating acrodermatitis enteropathica effectively.
2 citations,
June 2022 in “Life” A 14-year-old boy is the youngest person reported with a rare, benign tumor related to hair follicles, usually found in older people.
 January 2016 in “Chemistry & Industry”
January 2016 in “Chemistry & Industry” Two drugs, tofacitinib and ruxolitinib, may help regrow hair by activating hair follicles.
 10 citations,
April 1976 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
April 1976 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman's significant hair loss was linked to rapid weight loss and hormone injections.
 1 citations,
April 1976 in “Archives of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 1976 in “Archives of Dermatology” Sudden weight loss can cause significant hair loss, and using colchicine on the skin for psoriasis may be unsafe.
March 2022 in “JAAD case reports” Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of hair loss.
16 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Korean medical science/Journal of Korean Medical Science” A Korean boy's skin and digestive symptoms were caused by a rare genetic disorder that affects zinc absorption, and he got better with zinc supplements.
 August 2023 in “International Ayurvedic medical journal”
August 2023 in “International Ayurvedic medical journal” Ayurvedic treatment successfully regrew hair in a 7-year-old girl with alopecia areata.
August 2014 in “Chinese Journal of Dermatology” Scalp psoriasis in China mostly affects young adults, worsens with stress, and significantly impacts quality of life.
 1 citations,
October 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Tofacitinib improved hair loss and skin symptoms in a patient after secukinumab caused hair loss.
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Frontal fibrosing alopecia might be linked to autoimmune diseases.
 7 citations,
July 2014 in “BMJ case reports”
7 citations,
July 2014 in “BMJ case reports” A rare skin disorder, Ichthyosis with confetti, has no cure but treatment focuses on managing symptoms with moisturizers.
 1 citations,
July 1996 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
1 citations,
July 1996 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Routine thyroid tests for diffuse alopecia in women may not be necessary, but checking for iron deficiency anemia could be useful.
 8 citations,
January 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
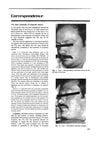
January 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” CO2 laser treatment successfully removed traumatic tattoos with minimal scarring.
 October 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
October 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Timely treatment and prevention are crucial to avoid serious complications in hair transplants.
 17 citations,
October 2003 in “Contact dermatitis”
17 citations,
October 2003 in “Contact dermatitis” Glycerin in hand cream can cause allergic skin reactions.
 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Colloids and surfaces. B, Biointerfaces” A new wound dressing with p-Coumaric acid helps heal diabetic wounds faster by reducing inflammation and promoting skin repair.
 1 citations,
August 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
1 citations,
August 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” A patient developed nerve problems as a side effect of a hair loss treatment called tofacitinib.
 June 2022 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
June 2022 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Microneedling with topical dutasteride improves hair growth in men with hair loss and is safe to use.
3 citations,
September 2019 in “European Medical Journal” Scalp sarcoidosis can cause hair loss and needs accurate diagnosis and treatment with specific medications.
 37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
37 citations,
October 2017 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib shows promise in treating atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata, but only slight improvement in vitiligo.






















