TLDR Tofacitinib improved hair loss and skin symptoms in a patient after secukinumab caused hair loss.
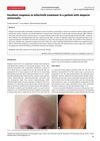
A 35-year-old female patient with Palmoplantar Pustulosis (PPP) developed Alopecia Areata (AA), a rare side effect, after treatment with secukinumab, a drug that targets interleukin-17 (IL-17). After discontinuing secukinumab and starting treatment with tofacitinib, both her AA and PPP significantly improved. The study suggests that tofacitinib could be a potential treatment for AA induced by biologics during PPP treatment. However, more research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm these findings.
28 citations
,
March 2018 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”  222 citations
,
September 2016 in “JCI insight”
222 citations
,
September 2016 in “JCI insight” Tofacitinib is safe and effective for severe alopecia areata, but hair loss may return 2 months after stopping treatment.
61 citations
,
June 2010 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Anti-TNF-α therapy may increase the risk of developing alopecia areata, especially in those with a history of autoimmune disease.

Tofacitinib helped a woman with total-body hair loss grow her hair back.
 1 citations
,
October 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
1 citations
,
October 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Tofacitinib improved hair loss and skin symptoms in a patient after secukinumab caused hair loss.
 24 citations
,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology”
24 citations
,
January 2018 in “International Journal of Trichology” Tofacitinib helped regrow hair in patients with alopecia, with few side effects.
 16 citations
,
July 2017 in “Rheumatology and Therapy”
16 citations
,
July 2017 in “Rheumatology and Therapy” Tofacitinib, a medication for arthritis, showed potential for treating severe hair loss in a small Brazilian case series, but more research is needed.
 16 citations
,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
16 citations
,
January 2017 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” A patient with complete hair loss regrew all her hair using tofacitinib.