 September 2023 in “Al-Azhar International Medical Journal /Al-Azhar International Medical Journal”
September 2023 in “Al-Azhar International Medical Journal /Al-Azhar International Medical Journal” Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy is safe and effective for treating obesity in children and teens.
13 citations,
March 2012 in “The American Journal of Surgery” Modified laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy effectively controls diabetes and treats obesity with minimal complications.
13 citations,
November 2015 in “Journal of anesthesia” A woman permanently lost hair on her scalp after a long surgery.
[object Object]  12 citations,
February 2007 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
12 citations,
February 2007 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” Hair transplantation techniques have improved over 12 years, with follicular unit grafting providing more natural results and potential future advances in automation and genetics.
 February 2024 in “Journal of Robotic Surgery”
February 2024 in “Journal of Robotic Surgery” The document concludes that surgical robots improve surgery and recovery but are costly and can stress surgeons due to less patient contact.
 21 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
21 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The review highlights the need for more research on transgender dermatology, the role of dermatologists in gender affirmation, and the effects of hormone therapy on skin and hair.

The case shows the difficulty in diagnosing certain conditions when standard tests are negative.
10 citations,
April 2014 in “Molecular and Clinical Oncology” Alopecia areata can be an early sign of Hodgkin’s lymphoma and may improve with lymphoma treatment.
 June 2023 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
June 2023 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” Weight loss from bariatric surgery improved certain skin conditions.
 1 citations,
July 2022 in “Case reports in endocrinology”
1 citations,
July 2022 in “Case reports in endocrinology” A 70-year-old woman with a malignant adrenal tumor improved after surgery and radiotherapy.
 8 citations,
August 2007 in “Histopathology”
8 citations,
August 2007 in “Histopathology” Different growth patterns in thyroid tumors are influenced by where cell growth and death occur.
 September 2009 in “European Urology Supplements”
September 2009 in “European Urology Supplements” After prostate removal surgery, higher initial prostate size was linked to higher urethral PSA levels and more severe male pattern baldness.
 1 citations,
November 2015 in “Cochrane library”
1 citations,
November 2015 in “Cochrane library” 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help treat urinary symptoms from an enlarged prostate.
 81 citations,
August 2014 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
81 citations,
August 2014 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Red light therapy is safe and effectively increases hair growth in women with hair loss.
 58 citations,
July 2007 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
58 citations,
July 2007 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Tattooing helps treat skin conditions, reconstruct nipple-areola, mark radiation fields, and locate lesions.
 March 2020 in “QJM: An International Journal of Medicine”
March 2020 in “QJM: An International Journal of Medicine” SVF and PRP improve hair loss, but SVF causes more side effects.
6 citations,
March 2021 in “Frontiers in surgery” A woman's symptoms of increased body hair and testosterone were caused by a rare adrenal tumor, which was removed successfully.

AI-assisted surgical robots improve surgery precision and safety.
 58 citations,
March 2013 in “Human Reproduction Update”
58 citations,
March 2013 in “Human Reproduction Update” Products should be called 'sperm-safe' only after thorough, well-designed tests.

The document listed various medical job opportunities with competitive benefits and living conditions.
 4 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Human Hypertension”
4 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Human Hypertension” Women experience more side effects and have worse blood pressure control from hypertension treatments than men, despite using different medications.
 July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mindfulness reduces anxiety and depression in skin disease patients; dermatologists and psychiatrists often lack confidence in treating psychodermatological conditions.
 June 1995 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics”
June 1995 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics” Women with hair loss have higher androgen levels, while men with early balding have altered androgen ratios.
 June 1995 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics”
June 1995 in “International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics” The new method showed that endometriotic tissue has lower estrogen receptor levels but similar progesterone levels compared to normal endometrium, with both following a similar cycle.
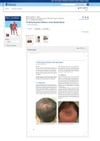
Hair restoration follows a specific pattern.
9 citations,
May 2022 in “Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience” Mesenchymal stromal cell therapies show promise for treating various diseases but need more research and standardization.
 March 2015 in “Polish Journal of Public Health”
March 2015 in “Polish Journal of Public Health” Blood vessel patterns in skin diseases relate to certain blood markers in systemic sclerosis but not in psoriasis or psoriatic arthritis, and may indicate circulation issues in alopecia.
 April 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
April 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Many women experience sexual dysfunction, but few seek help, and better treatment and medical training are needed.
 7 citations,
March 2011 in “Hormone and Metabolic Research”
7 citations,
March 2011 in “Hormone and Metabolic Research” Certain gene variations might help protect against insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in people with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
[object Object]  22 citations,
June 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
22 citations,
June 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A woman had both Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome, causing hair loss, and complete androgen insensitivity syndrome, making her genetically male but physically female. This suggests androgens don't affect the hair loss condition.

























