5 citations,
February 2022 in “Biophysical journal” The model shows that filament flexibility and amino acid differences affect how fast intermediate filament proteins assemble.
12 citations,
May 2021 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Laminin 332 is essential for normal skin cell behavior and structure.
 85 citations,
September 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
85 citations,
September 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Keratin 15 is not a reliable sole marker for identifying epidermal stem cells because it's found in various cell types.
1 citations,
July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Environmental factors can cause mutations in skin proteins, leading to skin disorders.
 October 2024 in “Frontiers in Oncology”
October 2024 in “Frontiers in Oncology” Keratin 18 helps diagnose and predict cancer progression and affects cancer growth and spread.
238 citations,
October 1994 in “Current opinion in genetics & development” The document concludes that recent research has improved understanding of skin diseases and the balance between cell growth and differentiation in the epidermis.
4 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of proteomics” Hair protein composition is similar across different races and shapes.
 40 citations,
May 2016 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
40 citations,
May 2016 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Changes in keratin make hair follicles stiffer.
38 citations,
November 2020 in “International journal of biochemistry & cell biology” Keratin proteins are essential for keeping the cells in the human colon healthy and stable.
 64 citations,
January 2010 in “The FASEB Journal”
64 citations,
January 2010 in “The FASEB Journal” Prolactin affects the production of different keratins in human hair, which could lead to new treatments for skin and hair disorders.
 7 citations,
July 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology”
7 citations,
July 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology” The study concluded that a protein important for hair strength is regulated by certain molecular processes and is affected by growth phases.
 48 citations,
July 1993 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
48 citations,
July 1993 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Hair growth is controlled by specific gene clusters and proteins, and cysteine affects hair gene expression in sheep.
 18 citations,
April 2014 in “Stem cells”
18 citations,
April 2014 in “Stem cells” The study found stem cells in minor salivary glands that can differentiate and are involved in tumor formation when exposed to tobacco.
 May 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
May 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The study found that certain genes are important for hedgehog skin appendage development and immunity, with spines possibly evolving for protection and infection resistance.
 7 citations,
March 2020 in “PloS one”
7 citations,
March 2020 in “PloS one” α-parvin is necessary for skin and hair growth and for the correct orientation of skin cells.
 December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” Keratin proteins are crucial for hair structure and strength.
 19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The protein p53 directly reduces the production of Keratin 17, a skin and hair protein, in rats with radiation dermatitis.

Keratin hydrogels from human hair show promise for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
 17 citations,
October 2017 in “Scientific reports”
17 citations,
October 2017 in “Scientific reports” Fine wool sheep have more genes for wool quality, while coarse wool sheep have more for skin and muscle traits.

Human hair keratins can self-assemble and support cell growth, useful for biomedical applications.
 2 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in genetics”
2 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in genetics” Different proteins are linked to the varying thickness of sheep and goat hair types.
 6 citations,
August 2023 in “BMC genomics”
6 citations,
August 2023 in “BMC genomics” The study found that genetic differences related to hair growth and other traits help cashmere goats adapt to high-altitude environments.
14 citations,
December 2016 in “PloS one” Keratin 26 affects cashmere goat hair growth and is influenced by various treatments.
 54 citations,
November 2015 in “Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology”
54 citations,
November 2015 in “Methods in enzymology on CD-ROM/Methods in enzymology” Keratins are important for skin cell health and their problems can cause diseases.
 May 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
May 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” KAP-depleted hair causes less immune response and is more biocompatible for implants.
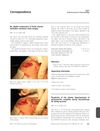 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 January 2023 in “Czech Journal of Animal Science”
January 2023 in “Czech Journal of Animal Science” Proteins influence the quality and traits of cashmere goat fleece, affecting hair strength and diameter.
68 citations,
December 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” HOXC13 is essential for hair and nail development by regulating Foxn1.
 30 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry”
30 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” Keratin 17 is modified by RSK1 in response to growth and stress, affecting skin growth and stress response.
 November 2023 in “Advanced Science”
November 2023 in “Advanced Science” A specific hair protein variant increases the spread of breast cancer and is linked to worse survival rates.





















