21 citations,
November 2015 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” There is no cure for alopecia areata, but treatments like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 12 citations,
December 2022 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
12 citations,
December 2022 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New oral treatments for adult hair loss show promise, especially JAK inhibitors, with mild side effects.
11 citations,
February 2022 in “JAAD case reports” Abrocitinib, a JAK inhibitor, may help treat atopic dermatitis and alopecia universalis together.
 7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors offer new hope for treating severe alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” JAK inhibitors are more effective and safer for treating alopecia areata than dupilumab and apremilast.
 1 citations,
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings”
1 citations,
December 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology. Symposium proceedings/The Journal of investigative dermatology symposium proceedings” Treating alopecia areata is difficult due to limited approved treatments, but new therapies like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 1 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologic therapy”
1 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologic therapy” JAK inhibitors show promise as a future treatment for hair loss.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan”
December 2024 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan” Vitiligo treatments include JAK inhibitors, UVB phototherapy, and dietary changes, with emotional support being important.
 December 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
December 2024 in “International Journal of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors may help treat both alopecia areata and vitiligo, but more research is needed.

Topical treatments like minoxidil and corticosteroids are effective for hair loss, with JAK inhibitors promising for alopecia areata.
 December 2024 in “Dermatological Reviews”
December 2024 in “Dermatological Reviews” New treatments for Alopecia Areata, like JAK inhibitors, are effective, and future research is exploring advanced therapies.
 April 2024 in “Expert opinion on investigational drugs”
April 2024 in “Expert opinion on investigational drugs” JAK inhibitors are safe and effective for treating moderate-to-severe alopecia areata.
 March 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
March 2024 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New treatments for severe alopecia areata, especially JAK inhibitors, are recommended as first-line therapy.
 January 2024 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal”
January 2024 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal” Early genetic testing and JAK inhibitors can help treat systemic inflammation in SAVI patients.
 August 2023 in “JAAD international”
August 2023 in “JAAD international” Pediatric dermatologists have varied preferences for treating alopecia areata in children, with no standard FDA-approved treatments and some using JAK inhibitors despite risks.
 June 2023 in “Fundamental & clinical pharmacology”
June 2023 in “Fundamental & clinical pharmacology” JAK inhibitors help treat some diseases but may increase risks of blood clots and cancer in certain patients.
 May 2023 in “Journal of managed care & specialty pharmacy”
May 2023 in “Journal of managed care & specialty pharmacy” Alopecia areata causes hair loss and life quality issues; current treatments are often unsatisfactory, but new drugs like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 April 2023 in “Revista colombiana de reumatología”
April 2023 in “Revista colombiana de reumatología” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib can effectively treat severe alopecia areata.

Alopecia Areata has no cure, treatments are limited, and the condition often recurs, but new therapies like JAK inhibitors show promise.
 February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata by reversing hair loss.
 June 2024 in “Bőrgyógyászati és Venerológiai Szemle”
June 2024 in “Bőrgyógyászati és Venerológiai Szemle” New treatments for hair loss, like JAK inhibitors, PRP, anti-androgens, and minoxidil, offer better options.
 157 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
157 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A man with vitiligo and alopecia saw quick skin and hair improvement with ruxolitinib, but skin color gains were lost after stopping treatment.
96 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA dermatology” Topical Ruxolitinib may safely treat severe hair loss.
 79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Oral tofacitinib can significantly improve recalcitrant lichen planopilaris.
 49 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib caused significant hair regrowth in adolescents with alopecia universalis who didn't respond to other treatments.
 48 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
48 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib 2% ointment helped hair regrow in 3 out of 10 patients with alopecia areata, but caused side effects like scalp irritation and raised cholesterol in some.
44 citations,
April 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” No treatment is completely effective for alopecia totalis and alopecia universalis.
 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
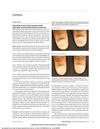
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 40 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
40 citations,
September 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped some young children with severe hair loss grow their hair back without bad side effects.
 39 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib may help treat severe childhood alopecia areata, but risks require careful consideration.

























