 February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia is caused by genetics, aging, and lifestyle, leading to hair follicle shrinkage and related health risks.
 9 citations,
August 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
August 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Scalp areas that look normal in people with hair loss may still show signs of disease under a microscope.
 November 2024 in “Deleted Journal”
November 2024 in “Deleted Journal” Platelet-rich plasma injections can help treat hair loss in lupus patients.
 2 citations,
March 2023 in “Skin research and technology”
2 citations,
March 2023 in “Skin research and technology” Temporal triangular alopecia in infants is mostly seen in males at birth, with unique features that help with diagnosis.
 23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
23 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” The study concluded that AAI and DAA are forms of the same disease, with different symptoms in men and women, and that corticosteroid treatment is effective.
 June 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
June 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Protein tyrosine kinases are key in male pattern baldness, affecting skin structure, hair growth, and immune responses.
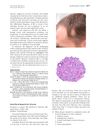
The man has Temporal Triangular Alopecia, a stable, non-scarring hair loss condition best treated with hair transplantation.
 158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology”
158 citations,
February 2000 in “Archives of dermatology” Some people with pattern hair loss may also have scalp inflammation and scarring similar to lichen planopilaris.
 December 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy”
December 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy” A man developed myasthenia gravis after alopecia areata, and treatment improved his symptoms and stopped hair loss.
 January 2018 in “The Kaohsiung journal of medical sciences”
January 2018 in “The Kaohsiung journal of medical sciences” A young man had a rare case of hair cysts on his elbows, which was hard to diagnose and treat.
 2 citations,
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology”
2 citations,
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology” Yellow dots and short vellus hairs are the most common signs of Alopecia Areata (AA), and trichoscopy can help diagnose AA and track treatment progress.
 14 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
14 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The document concludes that new methods improve the accuracy of diagnosing scalp alopecia and challenges the old way of classifying it.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” A condition with certain scalp changes may come before acne keloidalis nuchae and other similar hair loss disorders.
76 citations,
January 2011 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology/Indian journal of dermatology” Dermoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing and managing alopecia areata.
 33 citations,
January 2010 in “Case reports in dermatology”
33 citations,
January 2010 in “Case reports in dermatology” Dermoscopy helps diagnose frontal fibrosing alopecia by distinguishing it from other hair loss conditions.
 166 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
166 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Mostly postmenopausal Caucasian women get Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, which often includes eyebrow loss and has limited treatment success.
 20 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
20 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” Shrinking of oil glands in the skin is a key sign of hair loss linked to TNF inhibitor drugs and may improve if the treatment is stopped.
 13 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy”
13 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy” Alopecia areata causes varying hair loss patterns, affecting hair, nails, and possibly glands, with treatment outcomes depending on disease duration and extent.
 January 2024 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
January 2024 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Male gender and family history predict alopecia areata recurrence.
 2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus”
2 citations,
December 2022 in “PNAS nexus” SCD-153 shows promise as an effective topical treatment for alopecia areata.
 27 citations,
April 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
27 citations,
April 2017 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss involves immune responses, inflammation, and disrupted signaling pathways.
 October 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
October 2021 in “International journal of research in dermatology” No link between scalp patterns and alopecia severity in children, but more severe cases often had nail abnormalities.
 13 citations,
February 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
13 citations,
February 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The document concludes that recognizing specific histological features of different nonscarring alopecias is crucial for accurate diagnosis and understanding hair loss progression.
 160 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
160 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” New insights show Lichen Planopilaris is a rare, scarring hair loss condition, hard to treat, mainly affecting middle-aged women, and significantly impacts mental health.

The study concluded that Frontal fibrosing alopecia can affect younger people, is often missed in men, and may be autoimmune-related.
 17 citations,
May 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
17 citations,
May 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Reflectance confocal microscopy can help tell apart scarring from non-scarring hair loss.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne can appear or persist in adulthood due to hormonal changes, external factors, or substance use, and requires appropriate treatment.
 24 citations,
January 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
24 citations,
January 2012 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Diffuse alopecia areata involves more inflammation and higher allergy-related antibodies than patchy types.
19 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders” The report found a new type of hair loss in African-American women that affects more areas of the scalp than previously thought.
7 citations,
May 2021 in “Clinical Case Reports” Alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp are rare, treatable, and often resolve with doxycycline or on their own.



























