 July 2023 in “Veterinary pathology”
July 2023 in “Veterinary pathology” White-tailed deer can get a hair loss condition that might make them more vulnerable to environmental threats.
1 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Anti-Desmocollin 3 antibodies can cause pemphigus-like symptoms in mice.
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Targeting mTOR in myeloid cells may help reduce psoriasis symptoms.
 5 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
5 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” A brown shadow seen in dermoscopy is a marker for lichen nitidus.
 2 citations,
February 2019 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
2 citations,
February 2019 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Tufted folliculitis is common in patients with folliculitis decalvans.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Certain microRNAs may protect against hair loss in alopecia areata and could be potential treatment targets.
 33 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis”
33 citations,
June 2012 in “Journal of Crohn's and colitis” Alopecia Areata might be linked to Crohn's disease.
 May 2023 in “Surgical Case Reports”
May 2023 in “Surgical Case Reports” A woman's hair loss improved after removing a tumor in her thymus gland, suggesting hair loss can be linked to such tumors even without a specific muscle weakness condition.
 253 citations,
April 2014 in “Drugs”
253 citations,
April 2014 in “Drugs” Teriflunomide helps reduce multiple sclerosis symptoms and is safe for most patients.
 January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” The study concluded that a 'Swiss cheese' pattern in hair follicles is a useful sign for diagnosing alopecia areata.
 10 citations,
June 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Inflammation around hair follicles leads to hair loss, and treatments should focus on reducing this inflammation and other factors for effectiveness.
 April 2023 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
April 2023 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Lichen planus is a chronic autoimmune disease that is hard to treat and more common in women.
 33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” A fungal infection can look like a different scalp condition in teens, leading to wrong treatment until proper tests are done.
 9 citations,
April 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
9 citations,
April 2021 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Unconventional lymphocytes are important for quick immune responses and healing of skin and mucosal barriers.
 January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2007 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia areata is a reversible, autoimmune-related hair loss that can have significant emotional impact and uncertain treatment effectiveness.
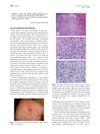 6 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
6 citations,
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman had a rare skin condition with recurring painful nodules that heal in 6 weeks, often without needing treatment.
 27 citations,
May 2007 in “Archives of dermatological research”
27 citations,
May 2007 in “Archives of dermatological research” Diphencyprone treatment increases CD8 lymphocytes in the scalp, which is associated with hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients.
January 2016 in “Indian dermatology online journal” The patient has frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA).
 7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology”
7 citations,
February 2015 in “Journal of comparative pathology” CD8+ T cells play a key role in graft-versus-host disease in certain mice models.
 88 citations,
August 2019 in “Nature communications”
88 citations,
August 2019 in “Nature communications” Researchers found a specific immune receptor in patients that causes severe skin reactions to a drug.
1 citations,
January 2022 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Lupus erythematosus can mimic alopecia areata, and trichoscopy is key for accurate diagnosis and better patient outcomes.
 5 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology”
5 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology” Increasing Treg cells in the skin does not cure hair loss from alopecia areata in mice.
 December 2020 in “Galen Medical Journal”
December 2020 in “Galen Medical Journal” People with Alopecia Areata and Androgenic Alopecia have more mast cells in their scalp than healthy individuals, especially those with Alopecia Areata.
 March 2019 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
March 2019 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” A man had both alopecia areata and lichen planus, which is uncommon.
August 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” ILC1-like cells can cause alopecia areata by disrupting hair follicle immunity, suggesting a new treatment approach.
 7 citations,
January 2011 in “Veterinary Pathology”
7 citations,
January 2011 in “Veterinary Pathology” A horse with severe hair loss was diagnosed with alopecia areata and a yeast infection.
 January 2024 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences”
January 2024 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences” Early intervention and patient education are crucial for managing alopecia areata.
 69 citations,
September 2006 in “Human Reproduction”
69 citations,
September 2006 in “Human Reproduction” Women with PCOS have fewer activated T cells in their ovarian follicles, which might affect fertility.
 148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
148 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of autoimmunity” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing patchy hair loss, often with other autoimmune disorders, but its exact causes are unknown.
December 2020 in “Galen Medical Journal” Alopecia patients have more mast cells in their scalps, especially in severe cases and older age, with alopecia areata showing the highest increase.
























