 June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Lower adrenal hormone levels may cause hair loss in postmenopausal women, certain patterns help diagnose nail cancer, and a gene variant linked to higher skin cancer risk in kidney transplant patients suggests monitoring folate levels.
 June 2023 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
June 2023 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New technologies show potential for better understanding and treating skin conditions with abnormal mucin, but more research is needed for clinical use.
 6 citations,
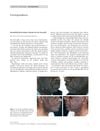
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.

Androgenetic alopecia, or hair loss, is caused by a mix of genetics, hormones, and environment, where testosterone affects hair growth and causes hair to become smaller and grow for a shorter time.
 May 2024 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
May 2024 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” A man with a type of skin lymphoma had unusual yellowish skin growths despite normal blood lipid levels, and treatment reduced some symptoms but not the growths.
 March 2019 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
March 2019 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” A man had both alopecia areata and lichen planus, which is uncommon.
 8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal”
8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal” A Korean woman with complete hair loss regrew her hair after taking tofacitinib, with no side effects.
17 citations,
January 2020 in “The World Journal of Men's Health” Long-term use of finasteride and dutasteride can cause serious health issues like diabetes and liver problems.
 59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science”
59 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Biomedical Science” Understanding how hair follicle stem cells work can help find new ways to prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
 5 citations,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
5 citations,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Certain mutations in the PADI3 gene may increase the risk of developing a type of scarring hair loss common in women of African descent.
 17 citations,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
17 citations,
August 2002 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Fluridil safely promotes hair growth in men with androgenetic alopecia.
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian journal of paediatric dermatology” Kids with alopecia areata had lower vitamin D levels than healthy kids.
 1 citations,
October 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” Skin stem cells can help improve skin repair and regeneration.
 August 2024 in “Current Protocols”
August 2024 in “Current Protocols” The C3H/HeJ mouse model is useful for studying and testing treatments for alopecia areata.
 October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology” New treatments and diagnostic methods for various animal skin conditions showed promising results.
 4 citations,
February 2016 in “Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics”
4 citations,
February 2016 in “Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics” Hair follicle samples effectively show how well the drug MK-0752 targets and engages with the Notch pathway.

Dupilumab helped improve skin and prevent new lesions in a child with a rare immune disorder and severe eczema.
 11 citations,
January 2023 in “BioMed Research International”
11 citations,
January 2023 in “BioMed Research International” Microbial biosurfactants could be a safer and environmentally friendly alternative to chemical surfactants in cosmetics.
 42 citations,
November 2018 in “Archives of dermatological research”
42 citations,
November 2018 in “Archives of dermatological research” Apremilast was not effective in treating moderate-to-severe alopecia areata.
 September 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1998 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Auto-portraits help evaluate scalp hair.
 January 2023 in “Applied sciences”
January 2023 in “Applied sciences” Gefitinib and Sasam-Kyeongokgo together significantly reduce cancer growth and improve immune response in mice.
 46 citations,
September 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
46 citations,
September 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride reduces Tourette syndrome symptoms, but results may be limited due to potential biases.
 2 citations,
November 2019 in “Cancer reports”
2 citations,
November 2019 in “Cancer reports” The Wnt signaling pathway is not a major factor in the development of keratoacanthoma, a type of skin tumor.
 47 citations,
June 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
47 citations,
June 2011 in “Movement Disorders” The LRRK2-G2019S mutation in Parkinson's disease has a lifetime penetrance of 25-35%, and finasteride may help reduce symptoms in adult male Tourette syndrome patients.
 31 citations,
June 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
31 citations,
June 2011 in “Movement Disorders” The document describes a woman with familial Parkinson's disease due to a genetic mutation, showing severe symptoms and poor response to treatment, and suggests finasteride may help reduce symptoms in Tourette syndrome.
 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Movement Disorders” THAP1 gene changes do not affect DYT1 dystonia; finasteride may help reduce tics and OCD in Tourette syndrome.
 5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride significantly reduced tics and obsessive-compulsive symptoms in Tourette syndrome patients.
 5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
5 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride may help reduce tic severity in male Tourette syndrome patients.
 39 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
39 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride may help reduce symptoms in male Tourette syndrome patients.
 17 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders”
17 citations,
May 2011 in “Movement Disorders” Finasteride significantly reduced tics and obsessive-compulsive symptoms in patients with Tourette syndrome.



























