
Human hair keratins can self-assemble and support cell growth, useful for biomedical applications.
[object Object] 10 citations,
November 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Sheep and goat hair fibers are complex due to keratin-associated proteins, which are important for fiber properties and growth.
70 citations,
January 2014 in “International review of cell and molecular biology” Keratin proteins are crucial for healthy skin, but mutations can cause skin disorders with no effective treatments yet.
 165 citations,
September 2001 in “Genes & development”
165 citations,
September 2001 in “Genes & development” CDP is crucial for lung and hair follicle cell development.
 89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics”
89 citations,
September 2010 in “Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics” The document concludes that understanding the genes and pathways involved in hair growth is crucial for developing treatments for hair diseases.
 19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The protein p53 directly reduces the production of Keratin 17, a skin and hair protein, in rats with radiation dermatitis.
[object Object]  9 citations,
April 2006 in “American Journal of Pathology”
9 citations,
April 2006 in “American Journal of Pathology” SGK3 is essential for proper hair growth and health.
 7 citations,
April 2012 in “Biomolecular concepts”
7 citations,
April 2012 in “Biomolecular concepts” Keratin is crucial for keeping skin cells healthy and its changes can lead to diseases and affect cell behavior.
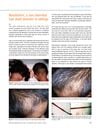 4 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
4 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian dermatology online journal” Monilethrix is a genetic hair disorder causing fragile, beaded hair with no effective treatment.
 42 citations,
January 2017 in “Genes”
42 citations,
January 2017 in “Genes” The gene KAP22-1 affects wool yield and fiber shape in sheep.
2 citations,
April 2021 in “FEBS open bio” Human hair keratins K85 and K35 create unique filament patterns important for early hair formation.
 36 citations,
November 2019 in “Molecular biology and evolution”
36 citations,
November 2019 in “Molecular biology and evolution” Cysteine-rich keratins evolved independently in mammals, reptiles, and birds for hard skin structures like hair, claws, and feathers.
 August 2019 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2019 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Certain long non-coding RNAs in cashmere goats affect hair growth when treated with a specific growth factor.
 January 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
January 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” New findings suggest potential treatments for melanoma, hyperpigmentation, hair defects, and multiple sclerosis, and show skin microbiome changes don't cause atopic dermatitis.
235 citations,
July 1999 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” Human hair is made up of different keratins, some strong and some weak, with specific types appearing at various stages of hair growth.
68 citations,
August 2014 in “PeerJ” Human hair proteins vary by individual, body site, and ethnicity, useful for forensics.
30 citations,
August 2008 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” TGase 3 helps build hair structure by forming strong bonds between proteins.
 26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New gene identification techniques have improved the understanding and classification of inherited hair disorders.
3 citations,
September 2014 in “SpringerPlus” Human hair loss may have evolved to help increase brain size.
 1 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Lipase H is important for hair follicle function and shaping hair fibers.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Forensic science international. Genetics”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Forensic science international. Genetics” Hair protein analysis might help identify a person's ethnicity, sex, and age in forensics.
 January 2023 in “Kafkas üniversitesi veteriner fakültesi dergisi/Kafkas üniversitesi veteriner fakültesi dergisi”
January 2023 in “Kafkas üniversitesi veteriner fakültesi dergisi/Kafkas üniversitesi veteriner fakültesi dergisi” Seasonal changes affect gene activity linked to hair growth in Angora goats.
 November 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
November 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Seasonal changes affect hair growth genes in Angora goats, possibly influencing mohair quality.
854 citations,
February 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Understanding hair follicle development can help treat hair loss, skin regeneration, and certain skin cancers.
69 citations,
January 2015 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research” Keratin mutations cause skin diseases and could lead to new treatments.
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Animals” A new goat gene affects cashmere fiber thickness; certain variations can make the fibers coarser.
 10 citations,
May 2020 in “Journal of proteome research”
10 citations,
May 2020 in “Journal of proteome research” Explosions don't stop hair proteins from being used to identify people.
 384 citations,
June 2005 in “Genes & development”
384 citations,
June 2005 in “Genes & development” β-catenin is essential for stem cell activation and proliferation in hair follicles.
 36 citations,
October 2000 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
36 citations,
October 2000 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A different gene near the hairless gene on chromosome 8p21 causes a rare hair loss condition in a German family.
25 citations,
November 2020 in “Experimental eye research/Experimental Eye Research” Different types of cells in the eye express specific keratins at various stages of development.



















