May 2024 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” Plant extracts can help prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
[object Object]  5 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
5 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Hair and skin healing involve complex cell interactions controlled by specific molecules and pathways, and hair follicle cells can help repair skin wounds.
 June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
June 2018 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair loss caused by genetics and hormones; more research needed for treatments.
 32 citations,
February 2024 in “Growth Hormone & IGF Research”
32 citations,
February 2024 in “Growth Hormone & IGF Research” Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) stops hair growth in mice by lowering a growth factor important for hair.
 77 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine”
77 citations,
March 2014 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine” Fat cells are important for healthy skin, hair growth, and healing, and changes in these cells can affect skin conditions and aging.
 47 citations,
May 1999 in “Reproduction”
47 citations,
May 1999 in “Reproduction” Goat reproductive activity and coat growth are affected by light and temperature, with temperature altering prolactin levels and hair growth, but not melatonin or estrus onset.
 68 citations,
June 2005 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets”
68 citations,
June 2005 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets” Oestrogens help maintain healthy skin, heal wounds, and may protect against skin aging and cancer.
 32 citations,
January 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Hormone therapy affects hair growth in transgender individuals, with testosterone potentially causing hair loss in trans men and estrogen reducing facial/body hair in trans women; treatment options vary.
 15 citations,
May 2020 in “BMC complementary medicine and therapies”
15 citations,
May 2020 in “BMC complementary medicine and therapies” Polygonum multiflorum extract helps hair grow longer and fights the effects of hormones that cause hair loss.
5 citations,
March 2022 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Colostrum-derived exosomes can promote hair growth and may be a promising treatment for hair loss.
 1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking a specific enzyme can reduce the negative impact of stress hormones on hair growth cells.
 11 citations,
December 2020 in “Notulae botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca”
11 citations,
December 2020 in “Notulae botanicae Horti Agrobotanici Cluj-Napoca” Mycorrhizal fungi and shading improve tea plant growth and nutrient uptake by changing hormone levels and gene expression.
August 2021 in “Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research” Plant extracts in shampoo improved hair thickness and density in men with hair loss.
 3 citations,
May 2014 in “InTech eBooks”
3 citations,
May 2014 in “InTech eBooks” Copper deficiency may cause hair loss, and treating it could involve nutrition and hormones.
 9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Topical L-thyroxine may help with wound healing and hair growth but should be used short-term due to potential risks.
 7 citations,
April 2012 in “Clinical investigation”
7 citations,
April 2012 in “Clinical investigation” Transdermal testosterone can improve sexual desire in postmenopausal women but lacks long-term safety data and is not FDA-approved for this use.
 3 citations,
January 2017 in “Yonsei Medical Journal”
3 citations,
January 2017 in “Yonsei Medical Journal” Blocking 11β-HSD1 can lessen the harmful effects of glucocorticoids on hair growth cells.
 36 citations,
February 2017 in “BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
36 citations,
February 2017 in “BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine” Geranium sibiricum extract helps hair grow and is more effective than minoxidil but can be toxic in high concentrations.
 November 2022 in “Cosmetics”
November 2022 in “Cosmetics” Red pigmented rice, like Sang-Yod rice, could help promote hair growth and prevent hair loss.
44 citations,
August 2008 in “Plant journal” D'orenone stops root hair growth by disrupting auxin transport, but adding auxin can reverse this.
 1 citations,
March 2022 in “Daehanhanuihakoeji”
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Daehanhanuihakoeji” Artemisia sieversiana extract may help prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
4 citations,
March 2022 in “Pharmaceutics” Regenerative cellular therapies show promise for treating non-scarring hair loss but need more research.
 5 citations,
November 2016 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine”
5 citations,
November 2016 in “Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine” BeauTop improves hair growth in androgenetic alopecia patients.
 4 citations,
August 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
4 citations,
August 2021 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Stress can cause hair loss by affecting nerve-related hair growth, and noradrenaline might help prevent this.
 3 citations,
September 2022 in “Molecules”
3 citations,
September 2022 in “Molecules” Camellia seed cake extract may help hair growth by blocking the hair loss effects of a hormone called DHT.
[object Object] 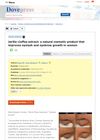 1 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Jarilla-Coffea extract gel effectively and safely increases eyelash and eyebrow thickness in women.
 17 citations,
April 2021 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual”
17 citations,
April 2021 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” Linoleic acid from Malva verticillata seeds may help treat hair loss by promoting hair cell growth and blocking baldness signals.
 2 citations,
December 2003
2 citations,
December 2003 Saw palmetto is an effective natural treatment for hair loss with minimal side effects.
 54 citations,
January 2013 in “BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
54 citations,
January 2013 in “BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine” Thuja orientalis hot water extract may help hair grow by starting the growth phase and improving hair follicle development.
 100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today”
100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today” Growth factors and cytokines are important for hair growth and could potentially treat hair loss, but more research is needed to overcome challenges before they can be used in treatments.
























