 24 citations,
March 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
24 citations,
March 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Treg dysfunction is linked to various autoimmune skin diseases, and understanding Treg properties is key for new treatments.
 58 citations,
August 2015 in “The Indonesian Biomedical Journal”
58 citations,
August 2015 in “The Indonesian Biomedical Journal” Different types of stem cells help maintain and heal skin.
 479 citations,
January 2005 in “BioEssays”
479 citations,
January 2005 in “BioEssays” Hair follicle development is controlled by interactions between skin tissues and specific molecular signals.
 January 2019 in “Advances in stem cells and their niches”
January 2019 in “Advances in stem cells and their niches” Skin health and repair depend on the signals between skin stem cells and their surrounding cells.
55 citations,
October 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” The review suggests that other immune cells besides CD8+ T cells may contribute to alopecia areata and that targeting regulatory cell defects could improve treatment.
 6 citations,
November 2013 in “International Journal of Radiation Biology”
6 citations,
November 2013 in “International Journal of Radiation Biology” Gamma-rays exposure during the resting phase of hair growth can damage hair regeneration and color in mice.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 15 citations,
June 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
June 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Hormones and genes affect hair growth and male baldness.
 12 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
12 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair follicle studies suggest that maintaining telomere length could help treat hair loss and graying, but it's uncertain if mouse results apply to humans.
2 citations,
October 2023 in “Science advances” Touching hair can activate nearby nerve cells through signals from the hair's outer layer.
 August 2023 in “Military Medical Research”
August 2023 in “Military Medical Research” Scientists have improved 3D models of human skin for research and medical uses, but still face challenges in perfectly replicating real skin.
 4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes”
4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes” Our microbiome may affect the development of the hair loss condition Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed to understand this relationship.
 98 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
98 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Prolactin affects hair growth and skin conditions, and could be a target for new skin disease treatments.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Stem cell research & therapy”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Stem cell research & therapy” Mesenchymal stem cells could help treat aging-related diseases better than current methods.
 218 citations,
January 2013 in “The Lancet Oncology”
218 citations,
January 2013 in “The Lancet Oncology” Chemotherapy causes hair loss by damaging hair follicles and stem cells, with more research needed for prevention and treatment.
 2 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Stem cells could improve hair growth and new treatments for baldness are being researched.
January 2024 in “Journal of developmental biology” Abdominal skin heals faster than dorsal skin because it has more stem cells.
 1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Understanding skin structure and development helps diagnose and treat skin disorders.
 8 citations,
January 2022 in “Burns and trauma”
8 citations,
January 2022 in “Burns and trauma” Skin cell-derived vesicles can help heal skin injuries effectively.
July 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” RF-based therapies might help treat hair loss.
 77 citations,
March 2021 in “Nature”
77 citations,
March 2021 in “Nature” Stress hormone corticosterone blocks a growth factor to slow down hair stem cell activity and hair growth.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Understanding how Regulatory T Cells work could help create treatments for certain skin diseases and cancers.
 127 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Biological Rhythms”
127 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Biological Rhythms” The skin's internal clock affects healing, cancer risk, aging, immunity, and hair growth, and disruptions can harm skin health.
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Microscopy research” Researchers successfully grew hair follicle stem cells from mice and humans, which could be useful for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
 137 citations,
April 2015 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
137 citations,
April 2015 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Different types of stem cells with unique roles exist in blood, skin, and intestines, and this variety is important for tissue repair.
 September 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
September 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Aging causes hair to gray and thin, with the timing of graying varying by race, and factors like oxidative stress and genetics can lead to hair loss.
 1 citations,
January 2021
1 citations,
January 2021 CD4+ skin cells may be precursors to basal cell carcinoma.
67 citations,
June 2019 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences” A new 3D culture system helps grow and study mouse skin stem cells for a long time.
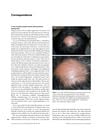 11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Greying hairs may be protected from alopecia areata.
 February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
February 2024 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Hair loss in Androgenetic Alopecia is caused by genetics, aging, and lifestyle, leading to hair follicle shrinkage and related health risks.
























