 39 citations,
May 2010 in “Stem Cells”
39 citations,
May 2010 in “Stem Cells” Ephrins slow down skin and hair follicle cell growth.
 222 citations,
October 2014 in “Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology”
222 citations,
October 2014 in “Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology” Eph receptors and ephrins may be promising targets for treating diseases, but more understanding is needed for effective and safe therapies.
 24 citations,
May 2016 in “Stem Cell Reviews and Reports”
24 citations,
May 2016 in “Stem Cell Reviews and Reports” The document concludes that understanding how adult stem and progenitor cells move is crucial for tissue repair and developing cell therapies.

Ovol2 is crucial for hair growth and skin healing by controlling cell movement and growth.
 25 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
25 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Genes linked to fibrosis are more active in people with central centrifugal cicatricial alopecia.
 3 citations,
January 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy”
3 citations,
January 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy” Lymphatic vessels are essential for health and can be targeted to treat various diseases.
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Molecules/Molecules online/Molecules annual” Cepharanthine has many medicinal uses but needs improvement for better effectiveness.
 30 citations,
April 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
30 citations,
April 2020 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” PI3K/Akt pathway is crucial for hair growth and regeneration.
 October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Immune cells are essential for early hair and skin development and healing.
 2 citations,
September 2023 in “Aging”
2 citations,
September 2023 in “Aging” Elastic Net DNA methylation clocks are inaccurate for predicting age and health status; a "noise barometer" may better indicate aging and disease.
 182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine”
182 citations,
November 2017 in “Molecular Aspects of Medicine” The PDGF/PDGFR pathway is a potential drug target with mixed success in treating various diseases, including some cancers and fibrosis.
 15 citations,
July 2008 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
15 citations,
July 2008 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Ephrin-A3 helps increase and speed up hair growth in baby mice.
 156 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of controlled release”
156 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of controlled release” Tight junctions are key for skin protection and controlling what gets absorbed or passes through the skin.
27 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of Autoimmunity” Human dermal γδT-cells respond to stress in hair follicles, contributing to hair loss.
 January 2022 in “Archiv für Tierzucht”
January 2022 in “Archiv für Tierzucht” EPHA4 and Ephrin A3 are found in the skin of Aohan fine-wool sheep.
 47 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
47 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Hair loss in balding individuals is linked to changes in specific hair growth-related genes.
 165 citations,
June 2007 in “European Journal of Cell Biology”
165 citations,
June 2007 in “European Journal of Cell Biology” Hair follicle stem cells are key for hair and skin regeneration, can be reprogrammed, and have potential therapeutic uses, but also carry a risk of cancer.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “Drug delivery system”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “Drug delivery system” Anti-aging treatments like hair transplants, minoxidil, and finasteride effectively promote hair growth.

Stem cells regenerate tissues and their behavior varies by environment, suggesting the hematopoietic system model may need revision.
55 citations,
August 2013 in “PloS one” Genetic differences between young and old Tan sheep explain why their fleece changes from curly to straight as they age.
 26 citations,
December 2020 in “Nature metabolism”
26 citations,
December 2020 in “Nature metabolism” Rapamycin treatment helps with mitochondrial disease by reducing PKC levels.
45 citations,
October 2015 in “BMC Genomics” Chicken feather growth involves specific genes and shares similarities with hair development.
 191 citations,
September 2011 in “Cell stem cell”
191 citations,
September 2011 in “Cell stem cell” Hair follicle stem cells use specific chromatin changes to control their growth and differentiation.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
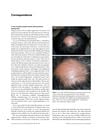 11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Greying hairs may be protected from alopecia areata.
 42 citations,
October 2011 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology”
42 citations,
October 2011 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology” Eph/ephrin signaling is important for skin cell behavior and could be targeted to treat skin diseases.
3 citations,
April 2019 in “Stem cells international” Markers CRABP1, Nestin, and Ephrin B2 are present in skin cancer environments and may influence their development.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Different levels of microRNAs in different parts of the scalp can cause male pattern baldness.

mEphA1 receptor tyrosine kinase is important for skin and hair development and may play a role in certain diseases.
 March 2009 in “Medical & surgical dermatology”
March 2009 in “Medical & surgical dermatology” Women with androgenetic alopecia have fewer terminal hairs, phenol in nail surgery is safe, and a new hair transplant method is faster and less damaging.

























