 186 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
186 citations,
July 1998 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Shorter CAG repeats may cause hair and skin issues, while longer ones may link to acne.
 38 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
38 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” EVG staining is a valuable, simple, and cost-effective method for diagnosing various skin conditions in dermatopathology.
 August 2001 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
August 2001 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Prednisone has risks for lupus patients, isotretinoin is safe for mental health, transplant patients risk skin cancer, and various treatments are effective for specific skin conditions.
 19 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
19 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The study found unique skin changes in a rare type of alopecia linked to a skin condition called linear morphea.
 9 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
9 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” People with pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus often have smaller sebaceous glands on their scalp.
 3 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
3 citations,
July 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” A woman's hair loss, resembling an autoimmune condition, improved after treatment, but requires ongoing checks due to potential serious associations.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Treating psoriasis with UVB light three times a week is faster than twice a week, and certain medications and lifestyle factors affect psoriasis treatment outcomes.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Skin problems are common in Bangladesh due to arsenic, prompt treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is crucial, maternal transmission causes most neonatal herpes, treatments for pediatric vasculitis are effective, the chickenpox vaccine works, more frequent UVB therapy helps psoriasis, certain jobs increase hand dermatitis risk, monoclonal antibodies treat psoriasis well, lifestyle affects psoriasis, alefacept improves psoriasis, imiquimod cream partially clears basal cell carcinoma, and iron may not help chronic hair loss.
 April 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
April 2024 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” Skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis can make it harder to correctly diagnose hair loss because they can cause the oil glands in the skin to shrink.
 31 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
31 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Hair becomes gray and thin as we age, and while most hair loss in older people is due to genetics, there's a chance for gray hair to regain color under certain conditions.
 April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” 848 genes related to fat and metabolism are less active in people with Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia.
 4 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2010 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Cicatricial alopecia involves scarring hair loss and can be treated with various medications.
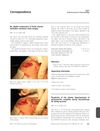 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 9 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of feline medicine and surgery”
9 citations,
November 2014 in “Journal of feline medicine and surgery” Lymphocytic mural folliculitis in cats might be an early sign of pancreatic cancer.
 7 citations,
September 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
7 citations,
September 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Some skin medications are safe for pregnant women, but others pose risks or should not be used.
 June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Lower adrenal hormone levels may cause hair loss in postmenopausal women, certain patterns help diagnose nail cancer, and a gene variant linked to higher skin cancer risk in kidney transplant patients suggests monitoring folate levels.
 30 citations,
October 2016 in “Current research in translational medicine”
30 citations,
October 2016 in “Current research in translational medicine” Hair follicles on the scalp interact with and respond to the nervous system, influencing their own behavior and growth.
 8 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic clinics”
8 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic clinics” New treatments for skin conditions in children include a preferred drug for birthmark reduction, proactive creams for eczema and vitiligo, a safe psoriasis medication, and special tissues and socks for eczema and fungal infections.
 January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2006 in “Elsevier eBooks” Cats with Feline Symmetrical Alopecia can regrow hair with proper treatment based on the specific cause, including diet, medication, or stress management.
 141 citations,
January 1984 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
141 citations,
January 1984 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause skin darkening, varicose veins, more sweating, hair growth, hair loss after birth, nail changes, and gum inflammation.
 96 citations,
January 1997 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
96 citations,
January 1997 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause skin pigmentation, stretch marks, and changes in hair, nails, and sweat glands, with most resolving after birth.
 39 citations,
March 2003 in “The Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice/Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice”
39 citations,
March 2003 in “The Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice/Veterinary clinics of North America. Small animal practice” Behavioral dermatology treats skin problems by considering both emotional and physical factors.
 37 citations,
August 2016 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
37 citations,
August 2016 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” The document concludes that better treatments for CCCA are needed and more research is required to understand its causes related to hairstyling and genetics.
 36 citations,
November 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
36 citations,
November 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Prolactin may affect hair growth differently based on gender and scalp area.
 34 citations,
November 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
34 citations,
November 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair extensions can cause hair loss and scalp damage, and these problems might be more common than people realize.
 28 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
28 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Lupus can look like hair loss from alopecia areata but needs different treatment.
 25 citations,
August 2007 in “Molecular Therapy”
25 citations,
August 2007 in “Molecular Therapy” Researchers found a safe and effective way to pick genetically modified skin cells with high growth potential using CD24.
 23 citations,
November 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology”
23 citations,
November 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology” Genetic discoveries are key for understanding, diagnosing, and treating inherited hair and nail disorders.
 20 citations,
July 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
July 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Obesity increases the risk of skin infections, inflammatory conditions, and melanoma, but not basal cell carcinoma.
 15 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
15 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Two plywood factory workers developed contact dermatitis from phenol-formaldehyde resin, a known allergen.






























