 June 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
June 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Different immune responses cause hair loss in scalp diseases, with unique patterns in scalp psoriasis possibly protecting against hair loss.
 83 citations,
June 2018 in “Frontiers in immunology”
83 citations,
June 2018 in “Frontiers in immunology” Certain types of T cells are essential for healthy skin and play a role in skin diseases, but more research is needed to improve treatments.
 47 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of immunology research”
47 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of immunology research” Valproic Acid could potentially be used to treat immune-related conditions due to its ability to modify immune cell functions.
[object Object]  April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, linked to genetic factors and immune system issues, with no cure yet.
91 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” NK cells play a role in skin diseases like eczema and psoriasis.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding the immune-related causes of Alopecia Areata has led to potential treatments like JAK inhibitors.
 56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine”
56 citations,
January 2021 in “Clinical and Experimental Medicine” The document concludes that while there are various treatments for Alopecia Areata, there is no cure, and individualized treatment plans are essential due to varying effectiveness.
46 citations,
October 2018 in “JCI insight” CD8+ T cells are involved in alopecia areata and may cause disease relapse.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “Frontiers in Immunology” New treatments for hair loss from alopecia areata may include targeting immune cells, using stem cells, balancing gut bacteria, applying fatty acids, and using JAK inhibitors.
 March 2024 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
March 2024 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Dandruff is linked to increased T cells and weakened immune protection in hair follicles.
75 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Alopecia areata can be triggered by specific immune cells without genetic or environmental factors.
253 citations,
December 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair follicles prevent NK cell attacks to avoid hair loss.
106 citations,
January 2013 in “Clinical and Developmental Immunology” Alopecia areata is caused by immune system attacks on hair follicles, often triggered by viral infections.
[object Object]  20 citations,
December 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
20 citations,
December 2019 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Blocking IL-12/IL-23 does not help with hair loss in alopecia areata for mice or humans.
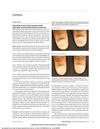 41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology”
41 citations,
December 2015 in “JAMA Dermatology” Tofacitinib citrate improved nail dystrophy and pain in patients with alopecia universalis without causing side effects.
 4 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert review of dermatology”
4 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert review of dermatology” Restoring immune privilege in hair follicles could help treat certain types of hair loss.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs” New treatments for hair loss show promise but need more research to confirm safety and effectiveness.
 14 citations,
March 2022 in “Journal of inflammation research”
14 citations,
March 2022 in “Journal of inflammation research” Baricitinib shows promise as a new treatment for certain skin conditions like alopecia areata.
 July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Ginseng, especially its component ginsenosides, can promote hair growth, reduce hair loss, and potentially treat conditions like alopecia by affecting cell pathways and cytokines.
 November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The study developed a mouse model for Alopecia Areata that responds to treatment, useful for future research.
 October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
October 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” A protein called EGFR protects hair follicle stem cells, and when it's disrupted, hair follicles can be damaged, but blocking certain pathways can restore hair growth.
 55 citations,
April 2010 in “Cancer and Metastasis Reviews”
55 citations,
April 2010 in “Cancer and Metastasis Reviews” TGFβ's manipulation of inflammation and immune cells affects cancer spread, suggesting new treatment strategies and biomarkers.
23 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Targeting Vδ1+T-cells may help treat alopecia areata.
 306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The skin has a complex immune system that is essential for protection and healing, requiring more research for better wound treatment.
50 citations,
May 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” Certain immune cells contribute to skin autoimmune diseases, and some treatments can reverse hair loss in these conditions.
 14 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
14 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Advanced therapies like gene, cell, and tissue engineering show promise for hair regrowth in alopecia, but their safety and effectiveness need more verification.
 3 citations,
October 2023 in “Military Medical Research/Military medical research”
3 citations,
October 2023 in “Military Medical Research/Military medical research” Regulatory T cells help heal skin and grow hair, and their absence can lead to healing issues and hair loss.
 December 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
December 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Aged individuals heal wounds less effectively due to specific immune cell issues.
 27 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
27 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Somatostatin may help protect hair follicles from immune attacks.
 11 citations,
October 2021 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
11 citations,
October 2021 in “Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Hair follicle stem cells reduced hair loss and inflammation in mice with a condition similar to human alopecia.























