 27 citations,
October 1945 in “Endocrinology”
27 citations,
October 1945 in “Endocrinology” Synthetic hormone treatment reduces melanin and hair growth in rats.
 13 citations,
March 2014 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
13 citations,
March 2014 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Minoxidil 5% solution significantly improved hair density in a girl with loose anagen hair syndrome over 28 months, with no side effects.
 February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata by reversing hair loss.
 17 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
17 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Flightless I protein affects hair growth, with low levels delaying it and high levels increasing hair length in rodents.
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Clinical & Cellular Immunology” Targeting CXCL10 may help treat alopecia areata.
 April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Many children with alopecia areata also have other autoimmune diseases.
12 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The MAGE3 hypothesis for alopecia areata did not lead to a significant breakthrough.
 2 citations,
June 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
2 citations,
June 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A critically ill boy experienced hair loss likely due to the stress of his medical treatments, but his hair regrew completely in 1.5 months.
 7 citations,
March 2002 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
7 citations,
March 2002 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” In 2002, hair restoration improved by using a different area for grafts and absorbable sutures, leading to less discomfort and better results.
August 2024 in “Steroids” The androgen receptor's shape-changing ability helps it function but can lead to cancer treatment resistance.
 28 citations,
April 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
28 citations,
April 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Genetic marker rs12558842 strongly linked to male hair loss.
 29 citations,
July 2008 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
29 citations,
July 2008 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Hair root sheaths are more common in non-scarring hair loss and help diagnose the type of hair loss.
 59 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
59 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The article explains the genetic causes and symptoms of various hair disorders and highlights the need for more research to find treatments.
 113 citations,
November 2017 in “Scientific Reports”
113 citations,
November 2017 in “Scientific Reports” Tiny particles from stem cells help activate hair growth cells and encourage hair growth in mice without being toxic.
 62 citations,
July 1993 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
62 citations,
July 1993 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair growth is influenced by interactions between skin layers, growth factors, and hormones, but the exact mechanisms are not fully understood.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that new treatments for hair loss may involve a combination of cosmetics, clinical methods, and genetic approaches.
 March 2023 in “Journal of clinical pharmacy and therapeutics”
March 2023 in “Journal of clinical pharmacy and therapeutics” Isoliensinine, a natural compound, prevents stress-related hair greying by blocking a specific receptor on hair cells.
 24 citations,
January 1993 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
24 citations,
January 1993 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil effectively treats hair loss, works better for women, and requires consistent use.
 12 citations,
April 2008 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
April 2008 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” There's no significant relationship between hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) and demodex infestation.
 90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
90 citations,
June 2006 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires careful examination of hair and scalp tissue, considering both clinical and microscopic features.
 3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” Possible causes of female hair loss include androgenetic alopecia, telogen effluvium, cicatricial alopecia, and alopecia areata incognita; diagnosis and treatment require dermoscopy and histopathology.
 15 citations,
January 2015 in “Pharmaceutical Biology”
15 citations,
January 2015 in “Pharmaceutical Biology” Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract may be a better treatment for hair loss than Minoxidil.
 9 citations,
January 2014 in “DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences”
9 citations,
January 2014 in “DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” Cuscuta reflexa extracts helped regrow hair in rats with drug-induced hair loss.
 21 citations,
January 2005 in “Skinmed”
21 citations,
January 2005 in “Skinmed” Hair and nails are similar keratin structures with different shapes and growth, affected by the same diseases and environmental factors.
 108 citations,
November 2006 in “Phytomedicine”
108 citations,
November 2006 in “Phytomedicine” Green tea component EGCG could potentially promote human hair growth.
 22 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
22 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil prolongs cell life, slows aging, and may produce longer hairs.
 78 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
78 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil promotes hair growth but stops working when discontinued.
 July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
July 2021 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Ginseng, especially its component ginsenosides, can promote hair growth, reduce hair loss, and potentially treat conditions like alopecia by affecting cell pathways and cytokines.
 36 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
36 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” White hair grows thicker and faster than black hair due to higher activity of growth-related genes and proteins.
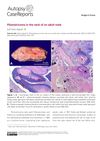 January 2022 in “Autopsy and Case Reports”
January 2022 in “Autopsy and Case Reports” A man had a non-cancerous neck tumor related to hair follicles removed with no return of the tumor.



























