 1 citations,
June 2023 in “JAAD case reports”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “JAAD case reports” Nivolumab treatment led to hair regrowth in a man with metastatic melanoma and alopecia areata.
February 2010 in “Emergency Medicine News” The woman has Discoid Lupus Erythematosus and needs specialist care.
63 citations,
July 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors can effectively reverse hair loss in people with alopecia areata.
40 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic clinics” More research is needed to understand the genetic causes of Alopecia areata to develop better treatments.
 61 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of Controlled Release”
61 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of Controlled Release” Dissolving microneedles show promise for delivering medication through the skin but face challenges like manufacturing complexity and regulatory hurdles.
 August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy”
August 2024 in “Indian Journal of Skin Allergy” Stem-cell therapy shows promise for skin conditions but needs more research.
 February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal”
February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal” Alopecia Areata affects people of all ages worldwide, is likely caused by genetic and environmental factors, and can lead to stress and depression, highlighting the need for treatments that address both physical and mental health.
 3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cutis”
3 citations,
June 2020 in “Cutis” Poor nutrition can lead to skin diseases in hospitalized patients and should be quickly identified and treated.
 October 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
October 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Dupilumab helped a 4-year-old grow hair back after another treatment failed.
 January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
January 2023 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” No single ideal JAK inhibitor for alopecia areata has been determined; JAK3 inhibitors may be promising with fewer side effects.
 January 2020 in “Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences”
January 2020 in “Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences” Certain immune molecules and stress affect hair loss, and while genes play a role, more research is needed to fully understand and treat it.
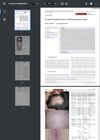 December 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy”
December 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy” A man developed myasthenia gravis after alopecia areata, and treatment improved his symptoms and stopped hair loss.
51 citations,
December 2017 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Stress may trigger hair loss by affecting immune protection in hair follicles.
16 citations,
June 2018 in “JAAD case reports” A JAK inhibitor improved both severe hair loss and chronic skin disease in one patient.
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Early diagnosis and quick treatment improve life quality for FFA patients.
 August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Imiquimod can cause rare skin side effects, some irreversible, and long-term follow-up is important for users.
 January 2021 in “Our Dermatology Online”
January 2021 in “Our Dermatology Online” Oral tofacitinib successfully treated total body hair loss in one patient.
 March 2022 in “Wound practice & research”
March 2022 in “Wound practice & research” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but standardized guidelines are needed.
488 citations,
July 2021 in “Cell” Fibroblasts are crucial for tissue repair and inflammation, and understanding them can help treat fibrotic diseases.
 January 2023 in “Clinical dermatology review”
January 2023 in “Clinical dermatology review” COVID-19 infection may cause hair loss.
 2 citations,
May 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports”
2 citations,
May 2022 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman lost all her hair after mild COVID-19, but it started to regrow after treatment with a specific medication.
 42 citations,
August 2013 in “International Journal of Women's Health”
42 citations,
August 2013 in “International Journal of Women's Health” Female pattern hair loss is caused by multiple factors and while treatments like topical minoxidil, hormone therapy, and low-level light therapy can help, none can fully cure it.
 1 citations,
January 2023 in “IDCases”
1 citations,
January 2023 in “IDCases” A patient experienced severe hair loss after getting an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
 4 citations,
August 2007 in “PubMed”
4 citations,
August 2007 in “PubMed” A woman lost all her body hair after hepatitis C treatment, but it started to grow back a year after stopping the treatment.
79 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata may be treated by restoring hair follicle immune privilege and adjusting immune responses.
20 citations,
November 2017 in “JAAD case reports” Ustekinumab significantly improved psoriasis, vitiligo, and alopecia areata in a patient.
137 citations,
January 2006 in “Frontiers in bioscience” CRH in the skin acts like the body's stress response system, affecting cell behavior and immune activity.
 2 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
2 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” T-regulatory cells are important for skin health and can affect hair growth and reduce skin inflammation.
 August 2024 in “EMJ Dermatology”
August 2024 in “EMJ Dermatology” Non-scarring alopecia in females affects emotional well-being and requires accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
ILC1-like cells can independently cause alopecia areata by affecting hair follicles.



















