 520 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS biophysics”
520 citations,
January 2017 in “AIMS biophysics” Photobiomodulation therapy using red and near-infrared light can reduce inflammation and aid in healing various conditions.
 January 2019 in “Clinical Dermatology Open Access Journal”
January 2019 in “Clinical Dermatology Open Access Journal” Combining corticosteroids and non-ablative fractional laser therapy may effectively treat extensive alopecia areata.
 6 citations,
January 2019 in “Medical Hypotheses”
6 citations,
January 2019 in “Medical Hypotheses” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia might be an autoimmune disease.
 9 citations,
October 2017 in “Translational pediatrics”
9 citations,
October 2017 in “Translational pediatrics” Pediatric endocrinologists should provide early fertility counseling and preservation options to young patients at risk of infertility.
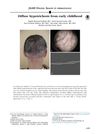 September 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The girl has a genetic hair condition causing thin hair since childhood.
 December 2023 in “Journal of General Procedural Dermatology and Venereology Indonesia”
December 2023 in “Journal of General Procedural Dermatology and Venereology Indonesia” A 61-year-old Filipino man had a skin condition that looked like another disease, making diagnosis difficult.
 23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology”
23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology” Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, is likely an autoimmune disease with a genetic link, but its exact cause is still unknown.
 4 citations,
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
4 citations,
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Lung and liver macrophages protect our tissues and their dysfunction can cause various diseases.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” FAPD and possibly CCCA may be AGA subtypes, and treatments combining antiandrogens, hair growth agents, hair transplants, and anti-inflammatories could be effective.

Low vitamin D3 is not linked to different levels of thyroid hormones in people with autoimmune thyroid disease.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Both atopy and eosinophilia are linked to more severe hair loss in people with alopecia areata.
 November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Injecting a person's own fat into their scalp may help regrow hair and improve hair thickness in different types of hair loss.
 1 citations,
December 2010 in “The journal of small animal practice/Journal of small animal practice”
1 citations,
December 2010 in “The journal of small animal practice/Journal of small animal practice” The book helps veterinarians understand and treat hair loss in animals.
 June 2006 in “Almustansiriya journal of pharmaceutical sciences/Al-Mustansiriyah journal of pharmaceutical sciences”
June 2006 in “Almustansiriya journal of pharmaceutical sciences/Al-Mustansiriyah journal of pharmaceutical sciences” Melatonin may help reduce the needed dose of prednisolone and improve hair growth in alopecia areata patients.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Mitochondrial dysfunction may contribute to chronic inflammation and immune system issues in Lichen planopilaris.

Tofacitinib may effectively treat hair loss and improve symptoms in autoimmune conditions like alopecia areata and Sjögren's syndrome, but long-term treatment might be necessary.
5 citations,
September 2022 in “Frontiers in Nutrition” Gut bacteria differences may help diagnose and treat Alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
September 2021 in “Curēus”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “Curēus” Tofacitinib may be safe for COVID-19 patients with alopecia without worsening symptoms, based on two cases.
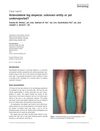 September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Anterolateral leg alopecia is a benign, nonprogressive hair loss condition on the lower legs that is not well understood and may resolve on its own.
January 2022 in “Exclusive Real World Evidence Journal” A rare form of lupus can cause severe nerve damage and other symptoms, but treatment can help.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Some cosmetic procedures show promise for treating hair loss, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
2 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Early onset, severe types, nail changes, family history, and body hair loss worsen alopecia areata prognosis; sticking to treatment helps.
 July 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
July 2023 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Hair loss can indicate various health issues, including serious diseases, hormonal imbalances, and can significantly affect personal life and mental health.
5 citations,
October 2012 in “Veterinary Pathology” A Doberman Pinscher had a rare form of autoimmune disease causing hair loss and other severe symptoms.
 34 citations,
October 2017 in “Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria”
34 citations,
October 2017 in “Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria” Alopecia Areata is a complex, unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited treatment options and a significant psychological impact.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with certain allergic conditions or higher white blood cell counts have more severe hair loss, and treating hair and nail side effects early in melanoma therapy can improve quality of life.
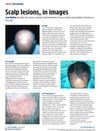 January 2015 in “Independent Nurse”
January 2015 in “Independent Nurse” Different scalp conditions can lead to hair loss or tumors, with treatments varying from creams to surgery; early detection is crucial.
 August 2021 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
August 2021 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Stress can trigger and worsen vitiligo.
 January 2023 in “International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences & Technology”
January 2023 in “International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences & Technology” Panchkarma treatment can help manage symptoms of Systemic Lupus Erythematous.
 7 citations,
December 2021 in “Pharmaceutics”
7 citations,
December 2021 in “Pharmaceutics” Natural products like plant extracts can help promote hair growth and could be used to treat hair loss.



























