 11 citations,
April 2019 in “Bioscience Reports”
11 citations,
April 2019 in “Bioscience Reports” Certain genetic variations in the RAB5B gene are linked to a higher risk of polycystic ovary syndrome in Chinese Han women.
 20 citations,
October 2008 in “European journal of endocrinology”
20 citations,
October 2008 in “European journal of endocrinology” Lower lipin 1β in belly fat is linked to insulin resistance in people with polycystic ovary syndrome.
 September 2023 in “Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology”
September 2023 in “Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology” JAGGED1 could help regenerate tissues for bone loss and heart damage if delivered correctly.
 38 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Endocrinology”
38 citations,
January 2014 in “International Journal of Endocrinology” Adrenal disorders can cause lasting brain and behavior issues in children.
 3 citations,
May 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine”
3 citations,
May 2021 in “Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine” Some traditional Chinese medicines may have anti-aging benefits and could help with hair growth, but more research is needed.
 123 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Neuroendocrinology”
123 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of Neuroendocrinology” New targets for making and using brain-synthesized steroids could lead to better treatments for brain disorders and alcoholism.
 103 citations,
March 2015 in “Nature Communications”
103 citations,
March 2015 in “Nature Communications” A genetic region near the PAX1 gene is linked to a higher risk of scoliosis in females.
 40 citations,
December 2012 in “Epilepsia”
40 citations,
December 2012 in “Epilepsia” Neurosteroids change how GABA_A receptors work in the brain, which could be important for treating temporal lobe epilepsy.
 49 citations,
November 2019 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics”
49 citations,
November 2019 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics” Certain gene variants may contribute to high androgen levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
 1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Understanding skin structure and development helps diagnose and treat skin disorders.
 10 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of Ovarian Research”
10 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of Ovarian Research” The IRS-2 Asp/Asp genotype may increase the risk of PCOS in Chinese women, especially if they are not obese.
 11 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
11 citations,
September 2019 in “Dermatologic Surgery” A substance called Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor can protect certain hair follicle stem cells from damage caused by androgens, suggesting a new possible treatment for hair loss.
 10 citations,
June 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” FP-1 is a key protein in rat hair growth, active only during the growth phase.
 13 citations,
October 2010 in “Pharmacogenomics”
13 citations,
October 2010 in “Pharmacogenomics” Researchers found that most genes affecting drug responses are not fully covered by commercial SNP chips, suggesting the need for more comprehensive tools to optimize drug selection based on genetics.
 15 citations,
February 2015 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research”
15 citations,
February 2015 in “Cell & tissue research/Cell and tissue research” P-cadherin is important for hair growth and health, and its problems can cause hair and skin disorders.
 54 citations,
December 2007 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
54 citations,
December 2007 in “Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Targeting glucocorticoid action might help treat type-2 diabetes, but human trials are needed.
 45 citations,
August 2010 in “Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation”
45 citations,
August 2010 in “Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation” Type 3 5α-reductase is more common and finasteride and dutasteride strongly inhibit it.
 August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Too much β-catenin activity can mess up the development of mammary glands and make them more like hair follicles.
 January 2001 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
January 2001 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Early signs of PCOS in girls, like irregular periods and polycystic ovaries, suggest a need for early diagnosis and intervention to prevent further health issues.
 128 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
128 citations,
September 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Obesity is linked to various skin problems and may increase the risk of skin cancer.
Editing the FGF5 gene in sheep increases fine wool growth.
218 citations,
September 2012 in “Gastroenterology” Colorectal cancer development involves both genetic changes and epigenetic alterations like DNA methylation and microRNA changes.
 October 2010 in “Reproductive Biomedicine Online”
October 2010 in “Reproductive Biomedicine Online” A new method can almost perfectly distinguish adenomyosis from similar conditions using blood tests.
 100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today”
100 citations,
November 1996 in “Molecular Medicine Today” Growth factors and cytokines are important for hair growth and could potentially treat hair loss, but more research is needed to overcome challenges before they can be used in treatments.
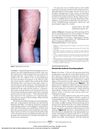 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride caused blisters on hands and feet.
 131 citations,
August 2004 in “Best Practice & Research in Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology”
131 citations,
August 2004 in “Best Practice & Research in Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology” The conclusion is that PCOS is caused by ovarian sensitivity to hormones and disrupted hormone control, possibly due to ovarian factors, and more research is needed.
 36 citations,
August 2018 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
36 citations,
August 2018 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing hair disorders without pulling out hair.
 August 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Borneol Essential Oil could be a natural and safe acne treatment.
 77 citations,
July 2013 in “Best Practice & Research in Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology”
77 citations,
July 2013 in “Best Practice & Research in Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology” Menopause reduces skin collagen and elasticity, and while estrogen therapy can help, its risks require careful consideration.
 38 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell and Tissue Research”
38 citations,
September 2014 in “Cell and Tissue Research” The hair follicle infundibulum plays a key role in skin health and disease, and understanding it better could lead to new skin disease treatments.



























