 December 1997 in “Proceedings of SPIE, the International Society for Optical Engineering/Proceedings of SPIE”
December 1997 in “Proceedings of SPIE, the International Society for Optical Engineering/Proceedings of SPIE” Low-energy laser therapy can improve scalp alopecia treatment when combined with classical methods.
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Higher CD70 and CD27 gene expression in alopecia areata lesions predicts disease severity and activity.
 January 2023 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
January 2023 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Platelet-rich plasma therapy is a safe and effective treatment for alopecia areata.
 19 citations,
May 2004 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
19 citations,
May 2004 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The research found that a specific gene mutation causes fewer hair follicles and disrupted hair growth cycles, leading to thin and short hair in people with Hypotrichosis with Juvenile Macular Dystrophy.
 13 citations,
March 2020 in “Genes”
13 citations,
March 2020 in “Genes” Disrupting the FGF5 gene in rabbits leads to longer hair by extending the hair growth phase.
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Targeting specific T cells may help treat alopecia areata.
 36 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
36 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Mice are useful for researching human hair loss and testing treatments, despite some differences between species.
 8 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology”
8 citations,
April 2020 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” Herbs might help with hair loss, but more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” ALRN-6924 can protect hair follicles from chemotherapy damage by temporarily stopping cell division.
 9 citations,
June 2020 in “BMC Molecular and Cell Biology”
9 citations,
June 2020 in “BMC Molecular and Cell Biology” Stress hormone CRF can cause hair loss by affecting hair growth cells and hormones.
 January 2024 in “Annals of Dermatology”
January 2024 in “Annals of Dermatology” Korean Red Ginseng may help protect hair from damage and promote growth.
ILC1-like cells may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata.
ILC1-like cells may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and could be new treatment targets.
 38 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
38 citations,
April 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding hair follicle cell cycles is crucial for hair growth and alopecia research, and recommends specific techniques and future research directions.
 30 citations,
July 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
July 2010 in “Experimental Dermatology” Polyamines are important for hair growth, but more research is needed to understand their functions and treatment potential.
 30 citations,
July 2017 in “BioEssays”
30 citations,
July 2017 in “BioEssays” Activating NRF2 might help treat hair disorders by improving antioxidant defenses.
 70 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation”
70 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation” The study identified and characterized new keratin genes linked to hair follicles and epithelial tissues.
 19 citations,
August 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets”
19 citations,
August 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets” New treatments for hair loss may target specific pathways and generate new hair follicles.
 10 citations,
January 2019 in “Biomarker Insights”
10 citations,
January 2019 in “Biomarker Insights” Scalp cooling to prevent hair loss from chemotherapy works for some but not all, and studying hair damage markers could improve prevention and treatment.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cell reconstitution after thymus transplantation can cause hair whitening and loss.
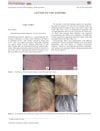 2 citations,
May 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
May 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Some patients' hair grew back black and white after chemotherapy.
 13 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
13 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The laser comb did not improve hair regrowth in mice with alopecia areata.
 81 citations,
October 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
81 citations,
October 2014 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Certain genes control the color of human hair by affecting pigment production.
 2 citations,
April 2022 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
2 citations,
April 2022 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” A new plant-based treatment was effective for hair regrowth in women with a specific type of hair loss that didn't respond to usual treatments.
 53 citations,
September 1999 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology”
53 citations,
September 1999 in “The journal of cell biology/The Journal of cell biology” K16 can partially replace K14 but causes hair loss and skin issues.
 22 citations,
January 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
22 citations,
January 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The meeting focused on understanding, diagnosing, and finding treatments for irreversible hair loss diseases.
 47 citations,
January 2019 in “Nature communications”
47 citations,
January 2019 in “Nature communications” Polyamines help fix DNA damage accurately in cells.
 9 citations,
October 2008 in “Mutation research”
9 citations,
October 2008 in “Mutation research” N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) can prevent DNA damage and protect cells from harm.
 March 2024 in “Stem cell research & therapy”
March 2024 in “Stem cell research & therapy” Human dental pulp stem cell-conditioned medium, especially from hypoxic conditions, may help treat chemotherapy-induced hair loss and does not increase cancer risk.
136 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” Dermal adipose tissue in mice can change and revert to help with skin health.

























