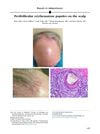
 January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The woman has a type of scarring hair loss with red bumps around hair follicles.
[object Object] The new minoxidil gel reduces runoff and improves eyebrow hair growth.
 26 citations,
March 1986 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
26 citations,
March 1986 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Scalp hair grows at 0.37 mm/day, forearm hair at 0.18 mm/day, and thigh hair at 0.30 mm/day, with no significant differences found in people with certain hair conditions.
 April 2024 in “Journal of wildlife diseases”
April 2024 in “Journal of wildlife diseases” Muskox hair growth rates vary widely, so a single growth rate can't be used for all populations.
 2 citations,
November 2017 in “PloS one”
2 citations,
November 2017 in “PloS one” Some vitamin D analogs can thicken skin and reduce pore size like a common acne treatment, with one analog also affecting skin growth factors.
 37 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology”
37 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology” ALA-photodynamic therapy helps reduce acne by causing acne cell death and lowering certain skin protein levels.
[object Object]  28 citations,
August 2003 in “Steroids”
28 citations,
August 2003 in “Steroids” Hirsute women have lower type 2 17β-HSD enzyme levels, which improve with treatment.
 22 citations,
October 2001 in “Biochemical Pharmacology”
22 citations,
October 2001 in “Biochemical Pharmacology” GI198745 is more potent and longer-lasting than finasteride, potentially better for treating hair loss.
 11 citations,
December 2011 in “Biochemical journal”
11 citations,
December 2011 in “Biochemical journal” Neurotrophin-4 increases calcium current in specific mouse neurons through the PI3K pathway.
 9 citations,
November 2012 in “Biomolecules & therapeutics”
9 citations,
November 2012 in “Biomolecules & therapeutics” A compound from brown algae boosts the production of a certain inflammatory substance in skin cells.
 5 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology”
5 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology” Increasing Treg cells in the skin does not cure hair loss from alopecia areata in mice.
 139 citations,
December 2020 in “Cell Stem Cell”
139 citations,
December 2020 in “Cell Stem Cell” Male hormones affect COVID-19 severity and certain drugs targeting these hormones could help reduce the risk.
 50 citations,
July 2021 in “Nature Communications”
50 citations,
July 2021 in “Nature Communications” The drug enzalutamide may reduce the ability of the virus causing COVID-19 to enter lung cells.
 40 citations,
June 2011 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry”
40 citations,
June 2011 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” FA2H is essential for normal fur and sebum production in mice.
 32 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
32 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice without certain skin proteins had abnormal skin and hair development.
 30 citations,
October 2020 in “Nature Communications”
30 citations,
October 2020 in “Nature Communications” Finasteride irreversibly affects human steroid 5α-reductase 2, providing insight into its catalytic mechanism and disease-related mutations.
 30 citations,
May 1999 in “Food and chemical toxicology”
30 citations,
May 1999 in “Food and chemical toxicology” Procyanidin B-2 is safe to use on skin as a hair growth product.
 27 citations,
June 2013 in “Genes & development”
27 citations,
June 2013 in “Genes & development” Cav1.2 affects hair growth and could be a target for hair loss treatments.
 17 citations,
October 2003 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research”
17 citations,
October 2003 in “Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research” The gene SDR5A1 is found in scalp hair of both hirsute and normal individuals, but it does not explain differences in hair growth.
 14 citations,
February 2018 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology”
14 citations,
February 2018 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology” Mice lacking steroid 5α-reductase 2 show less aggression and better impulse control.
 14 citations,
January 2006 in “Skin pharmacology and physiology”
14 citations,
January 2006 in “Skin pharmacology and physiology” Procyanidin compounds from apples and barley promote hair growth and prevent hair cell death.
 8 citations,
May 2018 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
8 citations,
May 2018 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” Activating the Nrf2 pathway reduces inflammation and cell activation in human hair follicles, suggesting a potential treatment for certain hair loss conditions.
 6 citations,
April 2014 in “European journal of medicinal chemistry”
6 citations,
April 2014 in “European journal of medicinal chemistry” New compounds similar to cromakalim were less effective at inhibiting insulin release but improved in solubility and one acted as a calcium entry blocker, not a potassium channel opener.
 July 2016 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
July 2016 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” The meeting showcased rare skin disease cases, highlighting the need for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 7 citations,
January 2014 in “Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin”
7 citations,
January 2014 in “Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin” Rice bran oil extracted by supercritical CO2 is considered non-genotoxic.
52 citations,
May 2011 in “APOPTOSIS” Hydroxyl radicals cause hair follicle cell death during chemotherapy by reducing Bcl-2 protein levels.
4 citations,
January 2020 in “Genes” The KRTAP21-2 gene affects wool length and quality in sheep.
2 citations,
August 2022 in “Animals” Different versions of the KRTAP6-2 gene in goats can lead to thinner cashmere fibers.
 10 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
10 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Higher DKK-1 levels found in hair loss patients; L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphate, L-threonate, and ginsenoside F2 may help promote hair growth.
3 citations,
February 2018 in “Experimental and Molecular Medicine/Experimental and molecular medicine” A protein called PCBP2 controls the production of a hair growth protein by interacting with its genetic message and is linked to hair loss when this control is disrupted.

























