 11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology”
11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology” Men are more likely to have severe respiratory viral infections like COVID-19 due to hormonal and genetic differences, while women generally have stronger immune responses.
 21 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science”
21 citations,
January 2022 in “Biomaterials Science” RNA delivery is best for in-body use, while RNP delivery is good for outside-body use. Both methods are expected to greatly impact future treatments.
71 citations,
January 2011 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” A rare skin condition was confirmed to be associated with a specific virus in a young girl.
14 citations,
February 2022 in “The Journal of clinical investigation/The journal of clinical investigation” Scientists made a mouse model of a serious skin cancer by changing skin cells with a virus and a specific gene, which is similar to the disease in humans.
2 citations,
December 2020 in “Frontiers in genetics” Researchers found genes linked to feather growth speed in Shouguang chickens, highlighting two genes that might explain differences in feathering.
19 citations,
August 2017 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Hepatitis B virus exposure may be linked to increased risk of alopecia areata.
 October 2018 in “Current Opinion in Genetics & Development”
October 2018 in “Current Opinion in Genetics & Development” The document emphasizes the importance of ongoing research and ethical considerations in genome editing and cellular reprogramming.
 2 citations,
January 2019 in “Medizinische Genetik”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Medizinische Genetik” The document reports findings on genetic research, including ethical concerns about genome editing, improved diagnosis of mitochondrial mutations, solving inherited eye diseases, confirming gene roles in epilepsy, linking a gene to aneurysms, and identifying genes associated with age-related macular degeneration.
 18 citations,
May 2020 in “Biomolecules”
18 citations,
May 2020 in “Biomolecules” Spironolactone, a heart and liver drug, has new uses including cancer treatment, viral infection prevention, and skin condition improvement.
 25 citations,
December 1995 in “Neurology”
25 citations,
December 1995 in “Neurology” The research found that chickenpox virus spreads in skin through blood then to skin cells, while shingles virus moves from nerves to hair follicle areas before infecting skin cells.
 24 citations,
May 2009 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
24 citations,
May 2009 in “Veterinary Dermatology” The document concludes that veterinary dermatologists need more experience and a better approach to treating skin diseases in nonhuman primates.
 21 citations,
April 2010 in “Molecular Medicine Reports”
21 citations,
April 2010 in “Molecular Medicine Reports” Zinc supplementation may help improve treatment outcomes for chronic hepatitis C.
 17 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics”
17 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics” COVID-19 may harm male fertility and damage the reproductive system.
 6 citations,
June 2019 in “Biotechnology Letters”
6 citations,
June 2019 in “Biotechnology Letters” Gene therapy shows promise for improving wound healing, but more research is needed for human use.
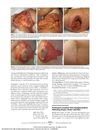 3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology” Herpes zoster infection can cause permanent hair color change in the affected area.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding the immune-related causes of Alopecia Areata has led to potential treatments like JAK inhibitors.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Evolutionary studies”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Evolutionary studies” Different human traits like skin color and hair type vary between populations due to genetic adaptations to the environment.
 April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik”
April 2023 in “Medizinische Genetik” New research has found 14 genes linked to the risk of developing alopecia areata, improving understanding and treatment options.
 6 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine”
6 citations,
October 2020 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” 3D culture helps maintain hair growth cells better than 2D culture and identifies key genes for potential hair loss treatments.
 1 citations,
March 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
March 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Low-coverage sequencing is a cost-effective way to identify genes related to wool traits in rabbits.
106 citations,
January 2013 in “Clinical and Developmental Immunology” Alopecia areata is caused by immune system attacks on hair follicles, often triggered by viral infections.
 4 citations,
April 2021 in “Experimental and Molecular Medicine”
4 citations,
April 2021 in “Experimental and Molecular Medicine” The conclusion is that certain genetic factors and blood types may affect COVID-19 severity, but changes in ACE2 and TMPRSS2 genes are not clearly linked to it.
 222 citations,
October 2014 in “Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology”
222 citations,
October 2014 in “Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology” Eph receptors and ephrins may be promising targets for treating diseases, but more understanding is needed for effective and safe therapies.
 99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology”
99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology” New treatments for Alopecia Areata show promise but need to be more effective and affordable.
 70 citations,
July 2020 in “Pharmacological Reports”
70 citations,
July 2020 in “Pharmacological Reports” Cepharanthine, a Japanese hair loss drug, shows promise as a COVID-19 treatment but needs more testing.
 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Journal of molecular evolution”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Journal of molecular evolution” Pangolins have lost some skin-related genes, but kept others, leading to their unique scales and skin features.
 1 citations,
July 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
July 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Keratin gene expression helps understand different types of skin cells and their development, and should be used carefully as biological markers.
 84 citations,
March 2010 in “Infectious Disease Clinics of North America”
84 citations,
March 2010 in “Infectious Disease Clinics of North America” The document concludes that rapid identification, isolation, and strict infection control are crucial to manage SARS outbreaks.
 60 citations,
June 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
60 citations,
June 1997 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Apoptosis is crucial for healthy skin and treating skin diseases.
 50 citations,
July 2021 in “Nature Communications”
50 citations,
July 2021 in “Nature Communications” The drug enzalutamide may reduce the ability of the virus causing COVID-19 to enter lung cells.
























