 16 citations,
January 2007 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
16 citations,
January 2007 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A man had an allergic reaction to minoxidil, which stopped after he discontinued use and started corticosteroids.
2 citations,
January 2009 A natural extract-based hair growth product was developed and showed promise in preliminary tests.
New treatments for skin diseases in 1979 showed promising results with fewer side effects.
3 citations,
January 2014 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Squaric acid dibutylester for alopecia areata can cause benign skin lymphoid growths.
 30 citations,
May 1999 in “Food and chemical toxicology”
30 citations,
May 1999 in “Food and chemical toxicology” Procyanidin B-2 is safe to use on skin as a hair growth product.
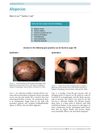 February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice”
February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice” Different types of alopecia in children require specific diagnoses and treatments.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman had a delayed allergic reaction to the blood thinner enoxaparin, treated with a steroid cream.
 April 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
April 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Some treatments work better for different types of hair loss, and nutrients like iron and L-lysine are important for preventing hair loss.
 January 1987 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 1987 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Some cosmetics and dermatological drugs can cause allergic reactions and side effects, like skin irritation and systemic issues.
 November 2000 in “Current problems in dermatology”
November 2000 in “Current problems in dermatology” New treatments for hair loss and excessive hair growth show promise with few side effects and advancements in laser technology.
 23 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
23 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Topical contact sensitizers can treat certain skin conditions but are rarely used in the U.K.
 12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research”
12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research” Lecithin-based microparticles can deliver minoxidil for hair growth effectively with less skin irritation.
 4 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
4 citations,
July 2008 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Poor response to topical immunotherapy in alopecia areata patients is linked to impaired cell responses.
 July 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences”
July 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” Diphenylcyclopropenone is more effective and has fewer side effects than dinitrochlorobenzene for treating alopecia areata.
 January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology” Many treatments for alopecia areata have inconsistent results; for under 10s, use minoxidil with a corticosteroid, and for over 10s, add ILC and consider diphenylcyclopropenone for widespread cases.
 188 citations,
October 2012 in “The AAPS Journal”
188 citations,
October 2012 in “The AAPS Journal” The document concludes that developing generic topical drugs requires ensuring they match the original in quality, composition, and structure, and often involves complex testing and regulatory steps.
 48 citations,
December 2013 in “Drug Delivery and Translational Research”
48 citations,
December 2013 in “Drug Delivery and Translational Research” Niosomes improve minoxidil skin penetration for hair loss treatment.
 45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology”
45 citations,
January 2010 in “International journal of trichology” Topical immunotherapy, especially with DPCP, is effective for treating severe alopecia areata.
 41 citations,
November 1993 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
41 citations,
November 1993 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” DPCP helps treat severe hair loss, but 5% minoxidil doesn't add benefits.
 39 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
39 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Ketoconazole cream is effective for skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and may help with hair loss and other skin issues, with generally mild side effects.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
 24 citations,
February 1987 in “Drugs”
24 citations,
February 1987 in “Drugs” Minoxidil promotes hair regrowth, but more research needed for effectiveness and response factors.
 23 citations,
April 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
April 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil solution can cause skin irritation and allergies in some users.
 21 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
21 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Topical DPCP is somewhat effective for hair loss in alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 20 citations,
March 1994 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
20 citations,
March 1994 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Too much topical minoxidil can cause excessive hair growth, but stopping treatment reverses it.
 16 citations,
December 2012 in “The Clinical Journal of Pain”
16 citations,
December 2012 in “The Clinical Journal of Pain” Chronic scalp pain in trichodynia involves both body-wide and localized increased pain sensitivity.
 16 citations,
January 1995 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
16 citations,
January 1995 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” SEPA™ enhances the effectiveness of minoxidil in stimulating hair growth, working faster and better than Rogaine® TS, with no significant side effects.
 15 citations,
November 2019 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology”
15 citations,
November 2019 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology” Minoxidil tretinoin liposomal based hydrogel shows promise for effective treatment of hair loss by delivering both drugs at the same time.
 9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” Topical L-thyroxine may help with wound healing and hair growth but should be used short-term due to potential risks.
 8 citations,
May 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
May 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” UV light does not significantly affect minoxidil's ability to treat male pattern baldness.



























