
Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with limited and variable treatment effectiveness.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “JAAD Case Reports” A woman with a type of hair loss saw hair regrowth after two months of taking baricitinib.
[object Object]  49 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tofacitinib caused significant hair regrowth in adolescents with alopecia universalis who didn't respond to other treatments.
 1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Curēus” Upadacitinib significantly improved a man's severe scalp condition when other treatments failed.
 99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology”
99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology” New treatments for Alopecia Areata show promise but need to be more effective and affordable.
 January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology”
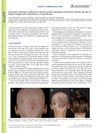
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” A condition called Central Centrifugal Cicatricial Alopecia causes hair loss and scalp burning in middle-aged African women, and it's treated with various medications, hair transplants, and non-drug methods like wigs.
 October 2024 in “JEADV Clinical Practice”
October 2024 in “JEADV Clinical Practice” UK dermatologists commonly use corticosteroids and minoxidil to treat hair loss conditions.
 24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
24 citations,
June 2016 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Tofacitinib helped a young woman's severe hair loss and arthritis but not her plaque psoriasis.
 37 citations,
May 2016 in “Deutsches Arzteblatt International”
37 citations,
May 2016 in “Deutsches Arzteblatt International” Hair loss requires customized treatments based on its various causes and types.
5 citations,
July 2020 in “Recent patents on inflammation & allergy drug discovery” Childhood Alopecia Areata causes hair loss and requires varied treatments, with psychological support being crucial.
[object Object]  1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 November 2024 in “Medicina”
November 2024 in “Medicina” Recognizing scalp symptoms in PRP is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
 August 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2023 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Early treatment is key for permanent hair loss disorders, with options ranging from medications and phototherapy to immunomodulators and antibiotics, depending on severity and type.
 October 2020 in “Revista médica sinergía/Revista médica sinergia”
October 2020 in “Revista médica sinergía/Revista médica sinergia” Alopecia areata is a complex condition causing hair loss, linked to genetics and immune system issues, and may be related to other autoimmune diseases; treatments vary in effectiveness.
 December 2023 in “European journal of dermatology/EJD. European journal of dermatology”
December 2023 in “European journal of dermatology/EJD. European journal of dermatology” More effective treatments are needed for severe alopecia areata.
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” A woman has a permanent hair loss condition treated with steroids and new medicines, but hair might not regrow.
 3 citations,
March 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Early treatment of Lupus Erythematosus Alopecia can prevent permanent hair loss, and various medications are effective.

Hair loss can be caused by hormones, illness, autoimmune disorders, or vitamin deficiencies, and treatments vary depending on the type.
 January 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine”
January 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine” New treatments for sudden hair loss include oral medications and a special laser, both showing promise in hair regrowth.
 April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Machine learning can predict how well patients with alopecia areata will respond to certain treatments.
 October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Comprehensive screening for infections is crucial before starting JAK inhibitors in alopecia areata patients.
 223 citations,
September 2018 in “Rheumatology”
223 citations,
September 2018 in “Rheumatology” JAK inhibitors are effective in treating various immune-related diseases, not just rheumatoid arthritis.
4 citations,
June 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” JAK inhibitors help hair regrowth in alopecia areata but have a high risk of side effects.
 1 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologic therapy”
1 citations,
November 2017 in “Dermatologic therapy” JAK inhibitors show promise as a future treatment for hair loss.
 116 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
116 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors help with skin conditions but need more research on dosing and safety.
 March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal”
March 2018 in “Suez Canal University Medical Journal” New drugs targeting the JAK-STAT pathway show promise for treating inflammatory skin diseases.
 January 2025 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine”
January 2025 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine” Baricitinib is effective and safe for treating localized vitiligo, alone or with topical tacrolimus.
 66 citations,
December 2018 in “Dermatology”
66 citations,
December 2018 in “Dermatology” Both ruxolitinib and tofacitinib are effective and safe for treating severe alopecia areata, but relapses are common.
 40 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology”
40 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in immunology” Blocking JAK/STAT pathways can help treat hair loss from alopecia areata.



























