 1 citations,
May 2023 in “Prospects in Pharmaceutical Sciences”
1 citations,
May 2023 in “Prospects in Pharmaceutical Sciences” New cytokine-targeted therapies show promise for treating alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)”
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Cochrane library (CD-ROM)” The analysis aims to identify the most effective and safest treatments for alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Melanocyte-associated antigens may play a key role in alopecia areata and could be targets for new treatments.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Side effects of drugs annual” The document concludes that various dermatological treatments and drugs can cause skin reactions and side effects.
 April 2024 in “Medical & clinical research”
April 2024 in “Medical & clinical research” More research is needed to find the best long-term treatments for Alopecia Areata.
 April 2024 in “Nepal journal of dermatology, venereology & leprology”
April 2024 in “Nepal journal of dermatology, venereology & leprology” Vitamin D is important for skin health and can help treat and prevent various skin conditions.
 January 2024 in “Burns and trauma”
January 2024 in “Burns and trauma” The skin microbiome helps heal wounds and can be targeted to improve healing.

Calcipotriene ointment improved a child's skin condition known as En coup de sabre.
 January 2023 in “Tehnika”
January 2023 in “Tehnika” Biomedical engineers are crucial for developing better treatments for chronic and autoimmune diseases.
 February 2022 in “Global academic journal of medical sciences”
February 2022 in “Global academic journal of medical sciences” People with alopecia areata have much lower Vitamin-D levels than healthy individuals.
 February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences”
February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences” No cure exists for alopecia areata, and treatments are personalized.
 January 2021 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2021 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” Ageratum conyzoides L. extract may effectively and safely treat hair loss.

Botulinum toxin type A significantly reduces scalp psoriasis severity compared to placebo.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia has significant social and psychological effects, leading to a market for hair loss treatments.
 April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” HSD11b1 affects skin nerves and increases non-histaminergic itch.
 January 2016 in “Kafkas Journal of Medical Sciences”
January 2016 in “Kafkas Journal of Medical Sciences” Turkish pregnant women commonly experienced skin issues like itching and acne, and doctors mainly used topical treatments due to safety concerns during pregnancy.
 August 2009 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
August 2009 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Pregnancy can cause skin changes and conditions that need correct diagnosis and treatment for the health of the mother and baby.
 June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2006 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The document reports unique growth lines in a child after Stevens-Johnson syndrome, skin reaction from parsnips and sun in a girl, and itchy skin with xanthomas in a boy with Alagille syndrome.
 March 2020 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology”
March 2020 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology” There's no significant link between blood fat levels and male pattern baldness.
January 2019 in “Egyptian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology /Egyptian Journal of Dermatology and Venerology” Mixing calcipotriol with a steroid is almost as effective as using a steroid alone for alopecia areata and has fewer side effects.
 June 2024 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology”
June 2024 in “Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology” TSLP affects atopic dermatitis by increasing sebum and reducing fat through IL-4/IL-13 signaling.
 1 citations,
December 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Tissue environment greatly affects the unique epigenetic makeup of regulatory T cells, which could impact autoimmune disease treatment.
 May 2022 in “Liver transplantation”
May 2022 in “Liver transplantation” The document explains how the immune system reacts to organ transplants and the treatments used to prevent rejection.
42 citations,
July 2013 in “Gene” IL-4 gene variation may increase the risk of alopecia areata in Turkish people.
 4 citations,
January 2023 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
4 citations,
January 2023 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Biologics, especially Dupilumab, are effective and safe for treating severe childhood eczema.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Einstein (São Paulo)”
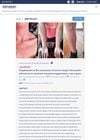
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Einstein (São Paulo)” Dupilumab improved severe atopic dermatitis in a patient who didn't respond to other treatments.
2 citations,
February 2023 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Baricitinib effectively improved both atopic dermatitis and alopecia areata symptoms in a patient.
 April 2023 in “Journal of dermatological treatment”
April 2023 in “Journal of dermatological treatment” Ixekizumab successfully treated a rare hair loss condition, leading to complete hair regrowth.
40 citations,
June 2021 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” JAK inhibitors show promise in effectively treating hair loss from alopecia areata.
12 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis” Certain IL-18 gene variations may increase the risk of alopecia areata.

























