 15 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 2020 in “Experimental Dermatology” The document concludes that understanding and treatments for alopecia areata have significantly advanced, now recognizing it as an autoimmune disorder.
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Blocking LFA-1 prevents hair loss in mice.
42 citations,
April 2021 in “JCI insight” Blocking JAK3 signaling can reverse hair loss from alopecia areata.
7 citations,
November 2018 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is caused by immune system issues, and JAK inhibitors might help treat it.
 January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
January 2025 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Hair follicles are key to treating vitiligo and alopecia areata, but challenges exist.
 6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity”
6 citations,
November 2022 in “Journal of autoimmunity” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib may effectively treat Alopecia Areata.
227 citations,
April 2020 in “Cell” More precise, personalized therapies are needed for autoimmune diseases.
18 citations,
June 2010 in “Cell Stress and Chaperones” Heat treatment increases hair loss in certain mice.
47 citations,
December 2011 in “Experimental Dermatology” CGRP may help protect hair follicles from immune system attacks, potentially slowing hair loss.
 62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
62 citations,
June 2015 in “The Journal of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata have more Th17 cells and fewer Treg cells, which may be key to the condition's development.
 3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
3 citations,
May 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Faulty inflammasome activation may lead to autoimmune skin diseases and could be a target for new treatments.
 January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology” A man had an unusual type of hair loss that didn't match known patterns and didn't improve with treatment.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 December 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
December 2012 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in the skin helps fat cell development during hair growth and repair.
 29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery”
29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition treated with corticosteroids, and histologic confirmation is the best diagnosis method.
 23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology”
23 citations,
January 2020 in “Central-European Journal of Immunology/Central European Journal of Immunology” Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, is likely an autoimmune disease with a genetic link, but its exact cause is still unknown.
 April 2015 in “Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences”
April 2015 in “Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences” People with autoimmune skin diseases often have hearing problems and should get their hearing checked early.
 January 2023 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences”
January 2023 in “International journal of homoeopathic sciences” The document says homoeopathic treatments are good for hair regrowth in alopecia areata but doesn't give proof.
 October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The most effective treatments for hair loss are minoxidil, finasteride, PRP, and hair transplants, with steroids and immunosuppressants for autoimmune types.
 3 citations,
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
3 citations,
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” CBD can either promote or inhibit hair growth depending on the concentration used.
 September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Blocking CCR5 can prevent and improve hair loss in alopecia areata.
 September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
September 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Human hair follicles have a unique way of using energy and might use the Cori cycle; blocking CCR5 could help treat hair loss.
 September 2023 in “Medical and Clinical Case Reports”
September 2023 in “Medical and Clinical Case Reports” People with Alopecia Areata often have thyroid problems like Hashimoto thyroiditis and hypothyroidism.
 April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Both induced and spontaneous AA lymphocytes can cause alopecia areata in mice.
 27 citations,
August 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
27 citations,
August 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hepatitis C virus can cause skin diseases and dermatologists play a crucial role in identifying these conditions.
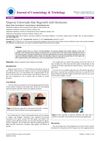 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology”
99 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical Reviews in Allergy & Immunology” New treatments for Alopecia Areata show promise but need to be more effective and affordable.
 70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Topical drugs and near-infrared light therapy show potential for treating alopecia.
 2 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy helped diagnose and treat a woman with two different types of hair loss.
 1 citations,
October 2013 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2013 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Diagnosing alopecia areata is challenging and requires careful examination and various tests to distinguish it from other hair loss types.
























