 April 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
April 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)” MSC-protein helps regenerate gum tissue and bone.
 January 2024 in “Frontiers in plant science”
January 2024 in “Frontiers in plant science” The zinc finger protein 3 in Arabidopsis thaliana reduces plant growth and root hair development.
 September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Dermal Papilla Cells grown in 3D and with stem cells better mimic natural hair growth conditions than cells grown in 2D.
[object Object]  15 citations,
July 2017 in “Hormones”
15 citations,
July 2017 in “Hormones” Genetic defects in the glucocorticoid receptor gene can cause conditions with abnormal sensitivity to stress hormones, and other factors may also affect this sensitivity.
 3 citations,
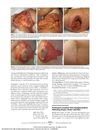
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2010 in “Archives of dermatology” Herpes zoster infection can cause permanent hair color change in the affected area.
 November 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
November 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Adipocytes can change into fibroblast-like cells to help with wound healing.
 8 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine”
8 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of Stem Cells & Regenerative Medicine” Dental pulp stem cells are better for tissue repair, while fat tissue stem cells may be more suited for wound healing and hair growth.
 95 citations,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
95 citations,
February 2019 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Mutations in the PADI3 gene are linked to a higher risk of scarring hair loss in women of African descent.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hair loss patterns differ between males and females due to 5 master regulators and JAK-STAT signaling affects hair growth.
 June 2024 in “Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy”
June 2024 in “Korean Journal of Pharmacognosy” The compound from Rhododendron mucronulatum roots may help treat male pattern hair loss.
 1 citations,
October 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
1 citations,
October 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Gene therapy shows promise for treating skin disorders and cancer, but faces technical challenges.
[object Object] 19 citations,
July 2020 in “EBioMedicine” A gene variant increases the risk of a type of hair loss by affecting hair protein production.
 21 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Rats can't grow new hair follicles after skin wounds, unlike mice, due to differences in gene expression and response to WNT signaling.
November 2022 in “Annals of Translational Medicine” Immune activities and specific genes are important in male pattern baldness.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Arrector pili muscle regulates hair follicle stem cells, DNA methylation needed for hair cycling, and Wnt/B-catenin signaling starts hair growth.
 19 citations,
June 2020 in “Animals”
19 citations,
June 2020 in “Animals” Poor maternal nutrition can lead to fewer wool follicles in Chinese Merino sheep.
 October 2022 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
October 2022 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” New tools show that in fish, NPY increases feeding and somatostatin decreases it.
 118 citations,
October 2013 in “Trends in Genetics”
118 citations,
October 2013 in “Trends in Genetics” The AUTS2 gene is linked to neurological disorders and may affect human brain development and cognition.
Genetic analysis of rabbits identified key genes for traits like coat color, body size, and fertility.
 11 citations,
March 2019 in “EMBO molecular medicine”
11 citations,
March 2019 in “EMBO molecular medicine” A defective protein in progeria causes cell death and atherosclerosis, but a treatment targeting cell stress may reduce these effects.
 6 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of nanobiotechnology”
6 citations,
February 2023 in “Journal of nanobiotechnology” The new anti-acne treatment HA-P5 effectively reduces acne by targeting two key receptors and avoids an enzyme that can hinder treatment.
 October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology” New treatments and diagnostic methods for various animal skin conditions showed promising results.
 211 citations,
May 2018 in “Trends in cell biology”
211 citations,
May 2018 in “Trends in cell biology” Different types of skin cells play specific roles in development, healing, and cancer.
 August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
August 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Too much β-catenin activity can mess up the development of mammary glands and make them more like hair follicles.
 29 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta neuropathologica communications”
29 citations,
April 2019 in “Acta neuropathologica communications” Stopping mitochondrial respiration can prevent brain cancer spread in skin cancer patients, and plant compound β-sitosterol could help achieve this.
 36 citations,
January 2019 in “Nature communications”
36 citations,
January 2019 in “Nature communications” High lactate dehydrogenase activity is not necessary for the growth of squamous cell carcinoma.
 6 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature cell biology”
6 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature cell biology” SOX9 helps determine stem cell roles by interacting with DNA and proteins that control gene activity.
 1 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature communications”
1 citations,
July 2023 in “Nature communications” MOF controls key genes for skin development by regulating mitochondrial and ciliary functions.
 3 citations,
January 2024 in “Liver International”
3 citations,
January 2024 in “Liver International” Targeting thyroid hormone receptor α in liver cells may help treat liver fibrosis.
44 citations,
February 2023 in “Cell” Fingerprints form uniquely before birth due to specific genetic pathways and local signals.


























