 January 1987 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 1987 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Some cosmetics and dermatological drugs can cause allergic reactions and side effects, like skin irritation and systemic issues.
 69 citations,
April 1998 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
69 citations,
April 1998 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Single hair grafting is effective for treating small, localized patches of vitiligo.
1 citations,
January 2007 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Dermatological treatments can have significant side effects, including allergic reactions, sexual dysfunction, and increased cancer risk.
144 citations,
December 2017 in “Pigment cell & melanoma research” Melasma is now considered a skin aging disorder caused by sun exposure in people with a genetic tendency, which impacts treatment and prevention approaches.
 21 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology”
21 citations,
January 2013 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” The combination of cyclosporine and PUVA might help treat severe alopecia areata.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “Expert opinion on orphan drugs” New treatments for hair loss show promise but need more research to confirm safety and effectiveness.
 8 citations,
May 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
May 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” UV light does not significantly affect minoxidil's ability to treat male pattern baldness.
 45 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology”
45 citations,
January 1998 in “Dermatology” Some skin conditions look like acne but are caused by drugs, and they usually get better when the drug is stopped.
 41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design”
41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design” Current and future treatments for alopecia areata focus on immunosuppression, immunomodulation, and protecting hair follicles.
 9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
9 citations,
July 2002 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that fexofenadine reduces inflammation in chronic hives, cholestyramine helps half of pregnant women with itchy rashes, and relaxing incisions are a good alternative in facial surgery for the elderly.
263 citations,
February 2020 in “International journal of molecular sciences” ADSCs help in wound healing and skin regeneration but need more research for full understanding.
 August 2024 in “Applied Sciences”
August 2024 in “Applied Sciences” Plant extracts may help prevent or reverse hair graying.
 February 1990 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 1990 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” New skin treatments in 1987-1988 showed effectiveness for various conditions, but some had side effects or risks.
 52 citations,
October 2016 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
52 citations,
October 2016 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Some medications can cause acne, and stopping these drugs is the main treatment.
 28 citations,
December 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
28 citations,
December 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Some medications might reverse gray hair, especially those that reduce inflammation or stimulate pigment production, and vitamin B might help.
 7 citations,
May 2014 in “Clinical practice”
7 citations,
May 2014 in “Clinical practice” Cooling the scalp may prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, hair often grows back after treatment, and nail issues usually improve after stopping the drug.
 4 citations,
August 2013 in “Case reports in dermatology”
4 citations,
August 2013 in “Case reports in dermatology” A patient with total hair loss developed vitiligo after using a treatment called DCP.

A patient's gum problems worsened after using cyclosporine for a scalp condition, but improved with a lower dose.
 January 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A man developed a painful skin condition after multiple heart procedures involving radiation.
 30 citations,
March 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology”
30 citations,
March 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride can cause one-sided breast enlargement, which disappears after stopping the drug.
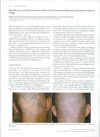 10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
10 citations,
January 2010 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Light therapy can effectively treat vitiligo and hair loss caused by a specific medication.
 January 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treating generalized granuloma annulare is difficult, with PUVA being the most effective option, but relapses are common.
 1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ” The document explains different hair and scalp conditions, including common hair loss after pregnancy or illness, drug-induced hair loss, hereditary excessive hair growth, patterned baldness, autoimmune hair loss, and permanent loss due to skin disease, with generally limited treatment options.
24 citations,
March 2009 in “Archives of dermatological research” The combination of oral PUVA and corticosteroids helps regrow hair in severe alopecia areata.
10 citations,
January 2012 in “Case reports in medicine” Diphencyprone can cause unexpected and possibly permanent vitiligo.
 25 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair regrowth slows with age and can be affected by treatments that change enzyme activity in the skin.
 2 citations,
April 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
April 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology” No treatment reliably changes Alopecia Areata's course; reassurance and possibly a wig are recommended.
 151 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
151 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss, has no cure, and various treatments exist.
 107 citations,
December 2003 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
107 citations,
December 2003 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Interferon, especially alfa interferon, is an effective treatment for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with manageable side effects.
 71 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery”
71 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery” Alopecia areata can cause unpredictable hair loss, and treatments like corticosteroids and minoxidil may help but have varying side effects.

























