21 citations,
January 2007 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Travoprost can help eyelash growth but may cause darkening around the eyes.
 5 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical Drug Investigation”
5 citations,
January 2019 in “Clinical Drug Investigation” Some off-label treatments increase hair density, but long-term safety unknown.

Human scalp hair follicles have PGE2 and its receptors, which might affect hair growth.
[object Object]  57 citations,
February 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology”
57 citations,
February 2014 in “Experimental Dermatology” Prostaglandin D₂ might be targeted for new male pattern baldness treatments.
 43 citations,
July 2013 in “Pharmacological reviews”
43 citations,
July 2013 in “Pharmacological reviews” New research on prostamide F2α has led to treatments for glaucoma and eyelash growth and may have more medical uses.
 January 2016 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
January 2016 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” A substance called prostaglandin D2 is found more in bald scalps and it stops hair from growing. Blocking its receptor could potentially treat hair loss.
 May 2012 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
May 2012 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Prostaglandin D2, found in higher levels in bald scalps, stops hair growth, suggesting that blocking its receptor could potentially treat hair loss.
 11 citations,
March 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology”
11 citations,
March 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology” A substance called compound-1 could help increase hair growth by maintaining prostaglandin levels in hair follicles.

L-PGDS has specific binding sites for its functions and could help in drug delivery system design.
 69 citations,
April 2010 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
69 citations,
April 2010 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Bimatoprost is a safe and effective treatment for making eyelashes longer, thicker, and darker.
 7 citations,
October 2006 in “Medical hypotheses”
7 citations,
October 2006 in “Medical hypotheses” UV light might cause excessive hair growth by increasing PGE2 in the skin.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Drugs & Therapy Perspectives” Use antiandrogens and other treatments for hair loss.
 53 citations,
October 2012 in “The FASEB Journal”
53 citations,
October 2012 in “The FASEB Journal” Bimatoprost, a glaucoma medication, may also help treat hair loss.
 38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
38 citations,
March 2017 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” Bimatoprost is promising for treating some types of hair loss but needs more testing for androgenetic alopecia.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Only minoxidil and finasteride are FDA-approved for hair loss, with other treatments available but less effective or with side effects.
 2 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis”
2 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis” A new method was developed to accurately detect and measure 47 different drug ingredients in various products.
January 2015 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Using travoprost for glaucoma may cause extra hair growth and darker skin around the eyes, but these effects can reverse after stopping the drug.
June 2013 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Central lipohypertrophy in HIV-infected women may lead to shorter eyelashes.
 January 2024 in “Biomedicines”
January 2024 in “Biomedicines” Using stem cells from hair follicles to treat female hair loss is safe and effective after six months.
[object Object]  16 citations,
November 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
16 citations,
November 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Prostanoids, like prostaglandins and thromboxane A2, can both enhance and inhibit hair growth, and understanding their effects could help treat hair disorders.
 81 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
81 citations,
August 2011 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Latanoprost 0.1% may effectively treat hair loss.
 65 citations,
November 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
65 citations,
November 2004 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Bimatoprost can cause excessive eyelash growth.
 58 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
58 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Male pattern hair loss caused by follicular miniaturization; early diagnosis and treatment can reduce psychological burden.
 36 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology”
36 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology” Bimatoprost was found to be safer and more effective than mometasone furoate for treating scalp hair loss.
 14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
14 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 9-year-old girl with alopecia areata had successful hair regrowth using bimatoprost after other treatments failed.
 12 citations,
December 2018 in “Clinical Ophthalmology”
12 citations,
December 2018 in “Clinical Ophthalmology” Latanoprostene bunod effectively lowers eye pressure and is better tolerated than other glaucoma medications.
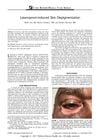 9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma”
9 citations,
November 2017 in “Journal of Glaucoma” Latanoprost eye drops may cause skin depigmentation.
 2 citations,
August 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
2 citations,
August 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Topical cetirizine 1% increases hair density and may be a promising treatment for hair loss.
 37 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Trichology”
37 citations,
January 2010 in “International Journal of Trichology” Bimatoprost helped eyelash growth in nearly half of the patients with a type of eyelash hair loss.
 33 citations,
January 2002
33 citations,
January 2002 Latanoprost, a glaucoma drug, showed potential for promoting hair growth in bald monkeys, especially at higher doses.


























