1 citations,
October 2015 in “The Pharma Innovation Journal” The best way to make a topical treatment for hair loss is to mix Saw Palmetto extract with 48% ethanol at the end of making the lotion.
[object Object]  August 2018 in “Reactions Weekly”
August 2018 in “Reactions Weekly” A woman had an allergic skin reaction to a hair loss treatment called minoxidil.
 April 2003 in “Reactions Weekly”
April 2003 in “Reactions Weekly” A woman developed skin irritation from treatments for hair loss, showing allergies to both minoxidil and saw palmetto solutions.
 May 1987 in “Inpharma (Balgowlah)”
May 1987 in “Inpharma (Balgowlah)” Topical minoxidil may slow hair loss but often doesn't lead to satisfactory hair regrowth and requires ongoing treatment.
 55 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of liposome research”
55 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of liposome research” New liposomal formulations may improve delivery of treatments to hair follicles, potentially helping with hair loss.
 52 citations,
February 1985 in “Archives of Dermatology”
52 citations,
February 1985 in “Archives of Dermatology” Minoxidil absorbs poorly through skin, with low risk of side effects at 1-2% concentration.
 39 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
39 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Topical minoxidil is a safe and effective treatment for hair loss caused by androgenetic alopecia.
 38 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
38 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Minoxidil can help grow hair and make hair follicles bigger, but it can also cause side effects.
 37 citations,
January 1987 in “Dermatology”
37 citations,
January 1987 in “Dermatology” Minoxidil stimulates hair growth by increasing hair thickness and prolonging growth phase.
 25 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry”
25 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry” Some herbal extracts, especially when used in cubosomal suspensions, were as effective as Minoxidil in promoting hair growth.
 25 citations,
November 1987 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
25 citations,
November 1987 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil didn't increase scalp blood flow for hair growth, but hexyl nicotinate did.
 23 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
23 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Ethosomal minoxidil improves hair growth by penetrating deeper into skin and shortening hair cycle.
 23 citations,
April 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
April 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil solution can cause skin irritation and allergies in some users.
[object Object]  22 citations,
April 2018 in “Pharmaceutics”
22 citations,
April 2018 in “Pharmaceutics” New methods improve how well skin treatments work by helping drugs get through the skin barrier.
 21 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
21 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Latanoprost may cause scalp inflammation and delayed healing.
 19 citations,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil can cause scalp comedones and acne.
 17 citations,
July 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
17 citations,
July 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil helps prevent hair loss from chemotherapy in rats.
 16 citations,
July 1986 in “Dermatology”
16 citations,
July 1986 in “Dermatology” Using minoxidil lotion for hair regrowth in androgenetic alopecia has limited success and should be evaluated carefully.
 14 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
14 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Some nonsurgical hair loss treatments are effective, especially if started early.
 12 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers”
12 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of Bioactive and Compatible Polymers” Nanoparticles show potential for controlled release of hair loss drugs, improving treatment effectiveness.
 12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research”
12 citations,
August 2017 in “Archives of Pharmacal Research” Lecithin-based microparticles can deliver minoxidil for hair growth effectively with less skin irritation.
 7 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
7 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Dermoscopy can't help doctors identify scalp irritation caused by topical minoxidil.
 7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Stopping imipramine reduced the woman's hair loss.
 3 citations,
January 2018
3 citations,
January 2018 A woman had an unusual allergic reaction to a hair loss treatment, which cleared up after stopping the treatment and using a different medication.
 3 citations,
July 2013 in “Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry”
3 citations,
July 2013 in “Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry” Chinese black tea extract helped mice grow hair, especially when combined with capsaicin.
 2 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology”
2 citations,
January 2009 in “Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology” Minoxidil in distearyldimethylammonium chloride vesicles significantly promotes hair growth, while minoxidil in microparticles or poloxamer solutions doesn't.
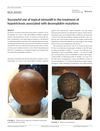 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology” Topical minoxidil helped an 8-year-old boy with a genetic hair disorder grow hair.
 January 2019 in “International Journal of Herbal Medicine”
January 2019 in “International Journal of Herbal Medicine” The polyherbal emulgel created for hair care was safe, had good qualities, and could lead to future hair care products.
 January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Minoxidil helps lower severe blood pressure and promotes hair growth but can have serious side effects and must be used continuously.

Glycyrrhizic acid and licorice extract can significantly reduce unwanted hair growth.




























