19 citations,
July 2017 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Men with lichen planopilaris had earlier onset than women, and treatment usually improved the condition.
 52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
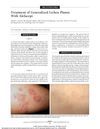
52 citations,
February 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” Alefacept may effectively treat severe lichen planus, with patients showing significant improvement and no side effects.
December 1977 in “Archives of Dermatology” Most patients with small patches of hair loss usually regrow hair.
 5 citations,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic therapy”
5 citations,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic therapy” Secukinumab for psoriasis unexpectedly caused increased hair growth in a patient.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.
 9 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental dermatology”
9 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental dermatology” Natural gene therapy shows promise for treating skin disorders like epidermolysis bullosa.
 19 citations,
March 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
19 citations,
March 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The gene Msx2 is crucial for hair follicle regeneration during wound healing.
 147 citations,
January 2003 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
147 citations,
January 2003 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of ichthyosis is crucial for treatment and genetic advice, and ongoing research is needed for better therapies.
 4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes”
4 citations,
October 2022 in “Genes” Our microbiome may affect the development of the hair loss condition Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed to understand this relationship.
 61 citations,
January 2017 in “Human Reproduction Open”
61 citations,
January 2017 in “Human Reproduction Open” The review recommends hormone replacement therapy for women with premature ovarian insufficiency to manage symptoms and protect health, with specific approaches for different groups.
 June 2017 in “Journal of clinical and investigative dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of clinical and investigative dermatology” Red blood cell folate levels are reliable indicators of long-term folate status in alopecia areata patients.

Different genes cause Female Pattern Hair Loss compared to male hair loss, and treatments vary, but more research is needed to understand it fully.
 April 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
April 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Lenalidomide helps hair follicle stem cells turn into melanocytes, which may improve repigmentation in vitiligo.
 99 citations,
August 2009 in “Nature Genetics”
99 citations,
August 2009 in “Nature Genetics” Removing both Atr and Trp53 genes in adult mice causes severe tissue damage and death due to DNA damage.
 39 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Asian hair is generally straight and thick, with unique disorders and properties, and more research is needed to understand it fully.
1 citations,
March 2022 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Higher CD70 and CD27 gene expression in alopecia areata lesions predicts disease severity and activity.
42 citations,
July 2013 in “Gene” IL-4 gene variation may increase the risk of alopecia areata in Turkish people.
88 citations,
August 2014 in “PLOS genetics” Syndecan-1 is essential for maintaining skin fat and preventing cold stress.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding the immune-related causes of Alopecia Areata has led to potential treatments like JAK inhibitors.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” A 73-year-old woman with Hypopigmented Mycosis Fungoides, a rare skin lymphoma, experienced disease progression despite treatment, emphasizing the need for ongoing monitoring.
 January 2017 in “Jikken doubutsu ihou/Jikken doubutsu/Experimental animals/Jikken Dobutsu”
January 2017 in “Jikken doubutsu ihou/Jikken doubutsu/Experimental animals/Jikken Dobutsu” Mice with a changed Hr gene lose and regrow hair due to changes in the gene's activity.
 38 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
38 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Accurate clinical, histological, and genetic methods are key for understanding and treating hair disorders.
 January 2015 in “Dermatology”
January 2015 in “Dermatology” The document covers various dermatological treatments and conditions.
 2 citations,
May 2017 in “International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences/International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences”
2 citations,
May 2017 in “International journal of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences/International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences” Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder caused by a specific gene mutation, characterized by aging symptoms and managed by monitoring heart health and using low-dose aspirin.
70 citations,
January 2014 in “International review of cell and molecular biology” Keratin proteins are crucial for healthy skin, but mutations can cause skin disorders with no effective treatments yet.
 7 citations,
January 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A genetic marker linked to a type of hair loss was found in most patients studied.
 2 citations,
December 2016 in “Experimental cell research”
2 citations,
December 2016 in “Experimental cell research” The research found a way to identify and study skin cells with stem cell traits, revealing they behave differently in culture and questioning current stemness assessment methods.
 61 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of Controlled Release”
61 citations,
June 2022 in “Journal of Controlled Release” Dissolving microneedles show promise for delivering medication through the skin but face challenges like manufacturing complexity and regulatory hurdles.
 109 citations,
December 1998 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
109 citations,
December 1998 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Manipulating the catagen and telogen phases of hair growth could lead to treatments for hair disorders.
 January 2022 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)”
January 2022 in “Acta dermatovenerologica Alpina, Pannonica et Adriatica (Tiskana izd.)” Uncombable hair syndrome causes frizzy hair and can affect the nervous system, eyes, and ears, often co-occurring with other hair, skin, nail, and teeth conditions, and is linked to three specific gene mutations.























