 1 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The "After Minoxidil" spray makes hair easier to style, less greasy, and encourages people to keep using the treatment.
1 citations,
March 2005 in “SKINmed/Skinmed” Oral contraceptives can help treat skin issues like acne and excess hair.
 April 2024 in “Liječnički vjesnik”
April 2024 in “Liječnički vjesnik” Modern treatments can effectively regrow hair and improve life for people with alopecia areata.
 March 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
March 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Combining genetic and physical trait analysis improves diagnosis accuracy for monogenic diabetes.
 February 2024 in “Frontiers in physiology”
February 2024 in “Frontiers in physiology” Lymphatic vessels are important for skin repair and could affect skin disease treatments.
 February 2024 in “IntechOpen eBooks”
February 2024 in “IntechOpen eBooks” Myo-inositol-based treatments greatly improve pregnancy chances for women with PCOS.
 January 2023 in “Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira”
January 2023 in “Revista da Associação Médica Brasileira” Brazilian patients with inflammatory bowel disease have a high rate of skin problems compared to healthy people.

New peptide biomaterials based on RADA16-I hydrogel can improve wound healing and could be used for tissue engineering.
October 2021 in “Brazilian Journal of Health Review” COVID-19 can cause skin issues like rashes and hair loss, which may last even after recovery.
 August 2021 in “Research, Society and Development”
August 2021 in “Research, Society and Development” Minoxidil slightly increased hair volume more than Finasterida, but both reduced hair loss similarly.
 December 2019 in “Medicina estética”
December 2019 in “Medicina estética” Dermoscopy is underused in aesthetic medicine, but it increases diagnostic confidence, and professionals need more training.
 December 2019 in “Medicina estética”
December 2019 in “Medicina estética” Dermoscopy is underused in aesthetic medicine, but it increases diagnosis confidence; more training is needed.

Changes in skin bacteria can affect hair loss and new treatments targeting these bacteria may prevent balding without sexual side effects.
 November 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
November 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy” A new topical solution safely reduces hair shedding by 38% on average by tightening a muscle in the scalp.
 January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” The document discusses various nail and hair disorders and their treatments.
 May 2015 in “Endocrinología y nutrición”
May 2015 in “Endocrinología y nutrición” The conclusion is that adult males with muscle weakness and hormonal imbalances should be tested for Kennedy's disease.
May 2022 in “Endocrine Abstracts” Cyproterone acetate therapy improved hair loss and reduced testosterone levels in a menopausal woman.
January 2022 in “Stem cell biology and regenerative medicine” Lymphatic vessels help hair follicles regenerate by interacting with stem cells.
 December 2017 in “PubMed”
December 2017 in “PubMed” Society's pressure to have children later in life favors genes that increase the risk of early baldness in male offspring.
 13 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
13 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Finasteride effectively stops hair loss in most patients, but concerns about rare sexual side effects exist.
5 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences” Finasteride can cause serious physical, mental, and sexual side effects, even after stopping the treatment.
 December 2023 in “EPRA international journal of multidisciplinary research”
December 2023 in “EPRA international journal of multidisciplinary research” Alopecia areata causes sudden hair loss, has genetic links, and can be managed but not cured.
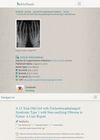 August 2022 in “Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics”
August 2022 in “Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics” A girl with a rare genetic disorder had a unique bone condition, highlighting the need for careful diagnosis and suggesting the disorder might be more common than thought.
August 2019 in “Archivos de medicina” Many students at the University of Manizales experience hair loss, needing urgent help.
May 2018 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” Mutations in the FOXN1 gene cause severe immune issues but don't affect hair and nails.
May 2017 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” Patients with certain FoxN1 gene mutations have severe immune issues but normal skin and hair.
 7 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2014 in “Journal of dermatology” Hair shaft miR-221 levels can help detect malignant melanoma.
 April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Both induced and spontaneous AA lymphocytes can cause alopecia areata in mice.
 108 citations,
July 2004 in “American Journal of Pathology”
108 citations,
July 2004 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress increases a factor in mice that leads to hair loss, and blocking this factor may prevent it.
 194 citations,
March 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology”
194 citations,
March 2003 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress stops hair growth in mice by causing early hair growth phase end and harmful inflammation through a specific nerve-related pathway.






















