 23 citations,
April 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
April 1991 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil solution can cause skin irritation and allergies in some users.
 23 citations,
March 1988 in “Biochemical Pharmacology”
23 citations,
March 1988 in “Biochemical Pharmacology” Minoxidil stops cells from making prostacyclin, which may help with hair growth. More research is needed.
 21 citations,
September 2001 in “Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
21 citations,
September 2001 in “Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” Minoxidil may help prevent capsular opacification after cataract surgery.
 21 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
21 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The study used monkeys to test a hair loss treatment called minoxidil, which showed positive results.
 19 citations,
March 1990 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology”
19 citations,
March 1990 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology” Minoxidil affects rat fluid dynamics, altering pressure and circulation, improving blood flow and hair growth.
 19 citations,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
19 citations,
December 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil can cause scalp comedones and acne.
 19 citations,
May 1979 in “Archives of internal medicine”
19 citations,
May 1979 in “Archives of internal medicine” Minoxidil effectively lowers blood pressure and initially increases plasma renin activity without raising aldosterone levels.
 17 citations,
April 2002 in “Contact Dermatitis”
17 citations,
April 2002 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil 5% caused skin discoloration in a man using it for hair loss.
 16 citations,
July 1986 in “Dermatology”
16 citations,
July 1986 in “Dermatology” Using minoxidil lotion for hair regrowth in androgenetic alopecia has limited success and should be evaluated carefully.
 15 citations,
November 2017 in “Drug Delivery and Translational Research”
15 citations,
November 2017 in “Drug Delivery and Translational Research” Certain extracts from Curcuma aeruginosa Roxb. and germacrone can boost the skin's absorption of minoxidil, a hair growth promoter, making it more effective.
 15 citations,
October 1981 in “Archives of internal medicine”
15 citations,
October 1981 in “Archives of internal medicine” Minoxidil can cause severe skin reactions like Stevens-Johnson syndrome in rare cases.
 14 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
14 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Human placental extract and minoxidil together significantly promote hair growth.
 14 citations,
July 1987 in “Contact Dermatitis”
14 citations,
July 1987 in “Contact Dermatitis” A small percentage of minoxidil users may develop an allergic skin reaction.
 13 citations,
November 2014 in “Pediatric emergency care”
13 citations,
November 2014 in “Pediatric emergency care” Ingesting minoxidil can cause serious heart issues; keep away from children and improve packaging.
 12 citations,
June 2012 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
12 citations,
June 2012 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Hair transplantation effectively treated a woman's patchy hair loss when other treatments failed.
 6 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of Dermatology”
6 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of Dermatology” Combination of 17α-estradiol and minoxidil improves hair growth and reduces hair loss in most patients.
 6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
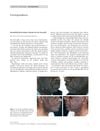
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 3 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” In Spain, dermatologists most commonly prescribe topical minoxidil and oral finasteride for male hair loss, and topical minoxidil and oral contraceptives for female hair loss. The use of oral dutasteride and oral minoxidil has significantly increased over the past three years.
 3 citations,
June 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
3 citations,
June 1997 in “Veterinary Dermatology” Minoxidil treatment can stimulate hair growth in hairless puppies if applied early.
 2 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Delaying hair loss treatment reduces its effectiveness.
 2 citations,
November 1987 in “Archives of Dermatology”
2 citations,
November 1987 in “Archives of Dermatology” Lotions release minoxidil better than creams, with a recommended mix of propylene glycol, water, and ethanol improving effectiveness.
 2 citations,
September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil caused hair to grow in unintended areas, like a tail, in a young girl.
 1 citations,
May 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil, when applied to the scalp, can stimulate hair growth but effects vary, stop if treatment ends, and it may cause side effects like fluid retention.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” A woman's severe hair loss was caused by scalp psoriasis, not the initially thought condition, and treatment improved her psoriasis but couldn't restore her lost hair.
 November 2000 in “Current problems in dermatology”
November 2000 in “Current problems in dermatology” New treatments for hair loss and excessive hair growth show promise with few side effects and advancements in laser technology.
 September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Cimetidine is not a first-choice treatment for female hair loss, and there's no consistently successful treatment for this condition in men or normal hormone level women.
 September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 1987 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Dr. Baral observed that applying minoxidil can cause hair to grow in areas other than where it was applied.
 November 2009 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
November 2009 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” Minoxidil and finasteride combined can effectively treat hair loss.
 370 citations,
September 1999 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
370 citations,
September 1999 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Finasteride and minoxidil are effective for hair loss, but continued research is needed for better treatments.
 268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
268 citations,
April 2009 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Niosomes improve minoxidil skin delivery for hair loss treatment.






























