 17 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
17 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Non-invasive methods show promise for diagnosing skin diseases like psoriasis and lupus but need more research for regular use.
 3 citations,
October 2022 in “Frontiers in Surgery”
3 citations,
October 2022 in “Frontiers in Surgery” Proteomics combined with other technologies can lead to a better understanding of skin diseases.
 277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The skin's layers protect, sense, and regulate the body's internal balance, but can be prone to cancer.
 40 citations,
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
40 citations,
January 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” The skin is the largest organ, protecting the body, regulating temperature, and producing hormones.
 788 citations,
February 2007 in “Nature”
788 citations,
February 2007 in “Nature” The document concludes that skin stem cells are important for hair growth and wound healing, and could be used in regenerative medicine.
 306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
306 citations,
April 2019 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The skin has a complex immune system that is essential for protection and healing, requiring more research for better wound treatment.
 18 citations,
September 2003 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
18 citations,
September 2003 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” VDUP1 is found in skin and hair follicles, interacts with sciellin, and may help regulate skin cell differentiation.
 74 citations,
June 2018 in “Cell death and disease”
74 citations,
June 2018 in “Cell death and disease” Restoring mitochondrial function in mice reversed their skin wrinkling and hair loss.
 40 citations,
January 2009 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
40 citations,
January 2009 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Fetal cells could improve skin repair with minimal scarring and are a potential ready-to-use solution for tissue engineering.
 17 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of pharmaceutical sciences”
17 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of pharmaceutical sciences” Researchers developed a nanomedicine for acne treatment that delivers medication with less irritation and is non-irritating for oily skin.

Proretinal nanoparticles are a safe and effective way to deliver retinal to the skin.
81 citations,
September 2009 in “Birth defects research” Different body areas in mice produce different hair types due to interactions between skin layers.

The new skin cream with zinc oxide nanoparticles is stable, spreads well, and doesn't deeply penetrate the skin.
 1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology”
1039 citations,
February 2009 in “Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology” Skin stem cells are crucial for maintaining and repairing the skin and hair, using a complex mix of signals to do so.
 47 citations,
March 2017 in “Materials Science and Engineering: C”
47 citations,
March 2017 in “Materials Science and Engineering: C” Human amniotic membrane helps heal skin wounds faster and with less scarring.
 39 citations,
November 2013 in “European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics”
39 citations,
November 2013 in “European journal of pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics” Massage increases how deep both rigid and flexible liposomes can go into skin, with flexible ones going deeper, and covering the skin (occlusion) helps rigid ones more.
 1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2016 in “Elsevier eBooks” Understanding skin structure and development helps diagnose and treat skin disorders.

Stem cells can improve skin grafts by enhancing blood flow and hair growth.
 137 citations,
January 2000 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
137 citations,
January 2000 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” The document recommends using both clinical evaluation and various measurement methods to assess skin greasiness, considering factors like temperature and hormones.
 2 citations,
May 2015 in “PloS one”
2 citations,
May 2015 in “PloS one” Hair follicle pores help cell survival and growth, even after radiation.
 November 2023 in “Linköping University medical dissertations”
November 2023 in “Linköping University medical dissertations” Keratinocytes and adipose-derived stem cells can effectively heal difficult skin wounds.

The skin is a complex barrier for drug penetration, but understanding its structure and interactions can improve drug delivery methods.
 22 citations,
November 2018 in “Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences”
22 citations,
November 2018 in “Brazilian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences” New physical methods like electrical currents, ultrasound, and microneedles show promise for improving drug delivery through the skin.
 133 citations,
May 2016 in “Cell Host & Microbe”
133 citations,
May 2016 in “Cell Host & Microbe” Human dermal fibroblasts are the main cells targeted by a virus that can cause a deadly skin cancer, and a certain inhibitor can effectively block this infection.
 6 citations,
December 2015 in “International journal of nanomedicine”
6 citations,
December 2015 in “International journal of nanomedicine” Using sonophoresis can make it harder for certain drug-loaded liposomes to get through the skin.
 38 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
38 citations,
December 2012 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” EVG staining is a valuable, simple, and cost-effective method for diagnosing various skin conditions in dermatopathology.
 6 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Stem Cell Research & Therapy”
6 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of Stem Cell Research & Therapy” Notch1 signaling is crucial for improving wound healing and skin regeneration by affecting stem cell behavior.
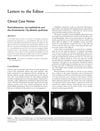 9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
9 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” The document discusses various eye conditions and their treatments, including a rare eye cancer in a baby, vision loss from a cancer drug, cataracts from a baldness treatment, a rare skin disorder, and a specific type of eye disease diagnosed with a special imaging technique.
 92 citations,
August 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
92 citations,
August 2017 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Newborn mouse skin cells can grow hair and this process can be recreated in adult cells to potentially help with hair loss.
 43 citations,
July 2019 in “Stem Cells International”
43 citations,
July 2019 in “Stem Cells International” Advancements in creating skin grafts with biomaterials and stem cells are promising, but more research is needed for clinical application.




























