 October 2024 in “Frontiers in Veterinary Science”
October 2024 in “Frontiers in Veterinary Science” FKBP10 and FBN2 are key proteins for hair growth in cashmere goats.
55 citations,
December 2021 in “BMC Veterinary Research” Certain genes in Iranian sheep are linked to wool production and heat adaptation.
[object Object] 8 citations,
August 2014 in “Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications” ODC overexpression in hair cells increases tumor growth by reducing Notch signaling.
 109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” New treatments targeting specific genes show promise for treating keratin disorders.
 July 2023 in “Drug testing and analysis (Print)”
July 2023 in “Drug testing and analysis (Print)” Homemade hair treatments can significantly lower drug levels in hair, possibly causing false-negative drug tests.
 9 citations,
January 1989 in “Sen'i Gakkaishi”
9 citations,
January 1989 in “Sen'i Gakkaishi” Wool and hair fibers absorb moisture similarly due to their keratin structure, with the amount of non-crystalline areas affecting the moisture uptake.
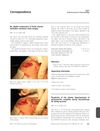 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 12 citations,
January 2014 in “Cell structure and function”
12 citations,
January 2014 in “Cell structure and function” Different combinations of human hair keratins affect how hair fibers form.
 9 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of Dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2017 in “Annals of Dermatology” The study found genetic differences related to hair development that may explain hair loss in a patient with Trichorhinophalangeal syndrome type I.
 16 citations,
December 2019 in “Animals”
16 citations,
December 2019 in “Animals” Overexpressing Tβ4 in goats' hair follicles increases cashmere production and hair follicle growth.
 6 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology”
6 citations,
November 2021 in “Frontiers in immunology” STAT3 signaling is important for healthy skin and hair follicles, and its disruption can lead to skin conditions like atopic dermatitis.
 13 citations,
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
13 citations,
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” Researchers created a lab model to study human hair growth, showing it can grow and self-regulate outside the body.
[object Object]  19 citations,
November 2018 in “Nutrients”
19 citations,
November 2018 in “Nutrients” Annurca apple extract may protect mouse hair from damage by chemotherapy and could help treat hair loss without promoting cancer growth.
 9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications”
9 citations,
February 2022 in “Nature communications” Rare changes in the KRT82 gene are linked to a higher risk of Alopecia Areata.
 17 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
17 citations,
December 2010 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Flightless I protein affects hair growth, with low levels delaying it and high levels increasing hair length in rodents.
11 citations,
October 2002 in “Genetics” A new mouse hair mutation, called hague, is semidominant and unstable, but the exact cause is unknown.
65 citations,
September 2014 in “BMC genomics” Different hair types in mammals are linked to variations in specific protein genes, with changes influenced by their living environments.
 April 2024 in “Skin appendage disorders”
April 2024 in “Skin appendage disorders” Environmental pollutants can damage hair health and cause hair loss.
 33 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
33 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Human hair follicle stem cells show signs of low oxygen levels, which may be important for hair growth and preventing baldness.
KRTAP6 genes affect wool quality in sheep.
 14 citations,
January 2015 in “Genetics and molecular research”
14 citations,
January 2015 in “Genetics and molecular research” The transition from growth to regression in Cashmere goat hair follicles involves changes in expression of genes related to keratin and cell differentiation.
 7 citations,
November 2022 in “Communications biology”
7 citations,
November 2022 in “Communications biology” Keratin injections can promote hair growth by affecting hair-forming cells and tissue development.
 5 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of applied polymer science”
5 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of applied polymer science” PEI diffuses into hair at a constant rate, and urea speeds up this process.
 62 citations,
January 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
62 citations,
January 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A second domain of high sulfur KAP genes on chromosome 21q23 is crucial for hair structure.
 53 citations,
July 2011 in “Biomaterials”
53 citations,
July 2011 in “Biomaterials” Human liver cells stick to hair protein materials mainly through the liver's asialoglycoprotein receptor.
 47 citations,
January 2017 in “RSC Advances”
47 citations,
January 2017 in “RSC Advances” Keratin peptides can change hair shape gently without harsh chemicals.
 26 citations,
May 2014 in “BioEssays”
26 citations,
May 2014 in “BioEssays” Using neurohormones to control keratin can lead to new skin disease treatments.
 7 citations,
February 1998 in “Polymer journal”
7 citations,
February 1998 in “Polymer journal” Keratin structure in hair is stable at pH 5-6 but disrupts between pH 6-7.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Certain mutations in the KLHL24 gene cause a skin disorder by breaking down an important skin protein.
 211 citations,
April 2018 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology”
211 citations,
April 2018 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology” Keratins are crucial for cell structure, growth, and disease risk.

























