
Stem cells regenerate tissues and their behavior varies by environment, suggesting the hematopoietic system model may need revision.
 May 2023 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
May 2023 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Thyroid disease can cause skin, hair, and nail problems, and treating the thyroid condition often improves these symptoms.
[object Object] 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of lipid research” Lipin-1 is important for skin cell differentiation and skin barrier function.
11 citations,
October 2002 in “Genetics” A new mouse hair mutation, called hague, is semidominant and unstable, but the exact cause is unknown.
1 citations,
January 2018 in “Indian dermatology online journal” The girl has both monilethrix and Type 1 diabetes, but no link between the two conditions is known.
 January 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
January 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Some cells may slow melanoma growth, a protein could affect skin pigmentation, a gene-silencing method might treat hair defects, skin bacteria changes likely result from eczema, and a defensin protein could help treat multiple sclerosis.
 3 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal of Biomedical Research/Journal of biomedical research”
3 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal of Biomedical Research/Journal of biomedical research” A new mutation in the KRT86 gene was found to cause the hair disorder monilethrix in a Han family.
 11 citations,
September 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
11 citations,
September 2012 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A mutation in the KRT71 gene causes a hair disorder by disrupting hair follicle structure and texture.
 42 citations,
October 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
42 citations,
October 2009 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Mutations in the KRT85 gene cause hair and nail problems.
July 2020 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A mutation in the KRT82 gene is significantly associated with Alopecia Areata.
27 citations,
November 2007 in “Genomics” Mutations in specific keratin genes cause improper hair structure in mice due to faulty keratin protein assembly.
 17 citations,
November 2017 in “Asian-Australasian journal of animal sciences”
17 citations,
November 2017 in “Asian-Australasian journal of animal sciences” Certain gene mutations are linked to wool quality in sheep and could help in breeding for better wool.
5 citations,
September 2018 in “International journal of genomics” Genetic mutations that disrupt homocysteine breakdown lead to increased damage in mouse hair keratin.
[object Object]  3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics”
3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics” A new type of pachyonychia congenita linked to a specific keratin gene mutation was found in two Pakistani families.
 November 2008 in “Medical & surgical dermatology”
November 2008 in “Medical & surgical dermatology” A device was made in 2008 to measure hair loss severity. Other findings include: frizzy mutation in mice isn't related to Fgfr2, C/EBPx marks preadipocytes, Cyclosporin A speeds up hair growth in mice, blocking plasmin and metalloproteinases hinders healing, hyperbaric oxygen helps ischemic wound healing, amniotic membranes heal wounds better than polyurethane foam, rhVEGF165 from a fibrin matrix improves tissue flap viability and induces VEGF-R2 expression, and bFGF enhances wound healing and reduces scarring in rabbits.
34 citations,
July 2020 in “American journal of human genetics” Changes in the SREBF1 gene cause a rare genetic skin and hair disorder.
 1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Genetic mutations cause various hair diseases, and whole genome sequencing may reveal more about these conditions.
 41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Some hair loss disorders are caused by genetic mutations affecting hair growth.
27 citations,
July 1997 in “PubMed” The harlequin ichthyosis mouse mutation causes thick skin and early death, resembling a human skin disorder.
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Animals” A new goat gene affects cashmere fiber thickness; certain variations can make the fibers coarser.
 November 2009 in “Medical & surgical dermatology”
November 2009 in “Medical & surgical dermatology” The document concludes that Borrelia afzelii causes a skin condition in France, a gene is linked to hair loss in Caucasian women, and various genetic mutations affect skin diseases.
13 citations,
May 2001 in “Current problems in dermatology” Keratin proteins in epithelial cells are dynamic and crucial for cell processes and disease understanding.
44 citations,
January 2004 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Understanding genetic mutations helps diagnose and treat skin disorders like ichthyosis.
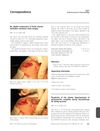 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Scientists have found specific genes linked to different hair loss conditions, which could lead to new treatments.
 6 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
6 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Using special RNA to target a mutant gene fixed hair problems in mice.
 6 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
6 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Chicken feather gene mutation helps understand human hair disorders.
 26 citations,
July 2012 in “Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects”
26 citations,
July 2012 in “Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects” The review found that different stem cell types in the skin are crucial for repair and could help treat skin diseases and cancer.
 31 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
31 citations,
August 2005 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” The study concluded that PKP1 is essential for skin integrity and hair growth, and its dysfunction causes the symptoms of ectodermal dysplasia/skin fragility syndrome.
 17 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
17 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that over 500 genes are linked to hair disorders and this knowledge is important for creating new treatments.



















