 182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
182 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some treatments can help with a hair loss condition called alopecia areata, but none ensure lasting results; choices depend on the person, with JAK inhibitors showing promise for severe cases.
 7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
August 2023 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors offer new hope for treating severe alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib may help regrow hair in severe alopecia areata, but results differ greatly between people.
 2 citations,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
2 citations,
April 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” A patient with alopecia had hair regrowth with tofacitinib but developed a skin reaction, choosing to continue the treatment despite the side effect.
 1 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
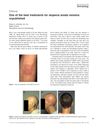
June 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” DNCB is highly effective for treating alopecia areata with minimal long-term side effects.
 16 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy”
16 citations,
June 2017 in “Advances in Therapy” New treatments for hair loss are showing promise due to better understanding of genetics and the immune system.
 1 citations,
May 2021 in “Annals of the rheumatic diseases”
1 citations,
May 2021 in “Annals of the rheumatic diseases” Tofacitinib is a promising treatment for children with rheumatic diseases.
 79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy”
79 citations,
September 2018 in “Dermatologic therapy” Oral tofacitinib can significantly improve recalcitrant lichen planopilaris.
 11 citations,
November 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
11 citations,
November 2019 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Oral tofacitinib is a promising treatment for beard hair loss in alopecia areata.
 290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
290 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, influenced by genetics, stress, and diet, and may be prevented by a high soy oil diet.
 April 2024 in “JEADV clinical practice”
April 2024 in “JEADV clinical practice” Upadacitinib significantly improved both rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia areata in a patient.
 7 citations,
April 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
April 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Topical tofacitinib may effectively and safely regrow facial hair in some people with alopecia areata.
 May 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
May 2023 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A potential treatment for atopic dermatitis could be to increase PADI1 expression to improve skin barrier function.

Different scalp and hair disorders are more common in certain ethnic groups, with the most common being androgenetic alopecia, which is treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride.
 2 citations,
January 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals”
2 citations,
January 2023 in “Pharmaceuticals” Natural products and phytochemicals may help with hair regrowth, but more research is needed.
2 citations,
April 2023 in “Polymers” The study created 3D-printed pills that effectively release a hair loss treatment drug over 24 hours.
 January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology”
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia, a common hair loss condition, can be treated with topical minoxidil, oral finasteride, or oral spironolactone, and new treatments like platelet-rich plasma, low-level laser therapy, and janus-kinase inhibitors are being explored.
September 2021 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses' Association” The convention discussed various skin conditions, treatments, and the importance of continuous learning in dermatology nursing.
 11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
December 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Stopping JAK inhibitor treatment for hair loss can lead to worse hair loss than before the treatment.
 April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Machine learning can predict how well patients with alopecia areata will respond to certain treatments.
 3 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib, a JAK inhibitor, improved hair regrowth in most patients with severe alopecia areata and had minimal side effects.
 October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
October 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Comprehensive screening for infections is crucial before starting JAK inhibitors in alopecia areata patients.
 7 citations,
April 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology”
7 citations,
April 2023 in “Frontiers in immunology” Oral baricitinib and ruxolitinib are effective and safe for treating alopecia areata.
 November 2017 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research”
November 2017 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research” Three compounds from Dadap leaves may help treat hair loss.
 February 2024 in “PloS one”
February 2024 in “PloS one” Tofacitinib and adalimumab are promising treatments for cicatricial alopecia with few side effects.
 February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
February 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” JAK inhibitors may help treat alopecia areata by reversing hair loss.
October 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology” JAK inhibitors do not improve hair regrowth in androgenic alopecia but may prevent further hair loss.
 6 citations,
March 2016 in “Scandinavian journal of immunology”
6 citations,
March 2016 in “Scandinavian journal of immunology” Janus kinase inhibitors show promise in treating alopecia areata but need more safety research.
 49 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Applying 2% tofacitinib cream helped some children with severe hair loss grow back hair.
 October 2024 in “Journal of Education Health and Sport”
October 2024 in “Journal of Education Health and Sport” Alopecia areata treatment should be personalized, using topical or systemic therapies based on severity, with promising options like JAK inhibitors needing more research.


























