 December 2015 in “Vascular Pharmacology”
December 2015 in “Vascular Pharmacology” Hair papilla cells are crucial for blood vessel development in hair follicles, affecting hair growth and loss.
 March 2019 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
March 2019 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” A man had both alopecia areata and lichen planus, which is uncommon.
 January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Pediatric alopecia areata is more immune-active than adult cases, suggesting age-specific treatments and potential use of JAK inhibitors.
 7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal”
7 citations,
October 2000 in “Allergo Journal” Stress may affect hair growth by influencing hair follicle development and could contribute to hair loss.
 22 citations,
June 2012 in “PLOS ONE”
22 citations,
June 2012 in “PLOS ONE” Cholesterol-related compounds can stop hair growth and cause inflammation in a type of scarring hair loss.
December 2020 in “Galen Medical Journal” Alopecia patients have more mast cells in their scalps, especially in severe cases and older age, with alopecia areata showing the highest increase.
January 2020 in “JAAD case reports” Hair loss condition FFA was seen before the appearance of skin depigmentation vitiligo in a patient.
14 citations,
August 2004 in “Veterinary Dermatology” The horse had a rare type of hair loss caused by immune cells attacking hair follicles.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of dermatology & cosmetology” Hyaluronic acid successfully treated skin atrophy caused by corticosteroid injections.
 7 citations,
February 2022 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
7 citations,
February 2022 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” Safflower oil nanoparticles can deliver hFGF10 to hair follicles, reduce inflammation, and potentially speed up hair growth in conditions causing hair loss.
March 2022 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Discoid Lupus Erythematosus causes scalp plaques that can lead to hair loss, and antimalarial drugs are effective treatments.
 3 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Trichoscopy helps tell apart Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Lichen planopilaris by showing different hair and scalp features.
 32 citations,
January 2006 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
32 citations,
January 2006 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” SACUMAN, a rare condition causing hair loss without clear signs, is often misdiagnosed and needs scalp biopsies for accurate detection.
 17 citations,
July 1994 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
17 citations,
July 1994 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The cause of alopecia areata is likely a mix of genetics, immune system issues, and environmental factors, with more research needed to understand it fully.
 2 citations,
March 2023 in “Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy”
2 citations,
March 2023 in “Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy” Platelet lysate effectively promotes hair growth and improves hair thickness in people with androgenetic alopecia.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Syphilitic alopecia is a rare hair loss condition in secondary syphilis that looks similar to another condition but can be diagnosed with specific tests and responds to antibiotics.
 131 citations,
November 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
131 citations,
November 1998 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin grafts on mice can cause an immune response leading to hair loss, useful for studying human hair loss conditions.
 April 2024 in “Skin appendage disorders”
April 2024 in “Skin appendage disorders” Environmental pollutants can damage hair health and cause hair loss.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne is linked to inflammation and insulin resistance, and is associated with various syndromes that require different treatments.
7 citations,
May 2021 in “Clinical Case Reports” Alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp are rare, treatable, and often resolve with doxycycline or on their own.
 November 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders”
November 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders” The document concludes that a woman has both Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia and Lichen Simplex Chronicus, a previously unreported combination of conditions.
 5 citations,
July 2013 in “Our Dermatology Online”
5 citations,
July 2013 in “Our Dermatology Online” Lichen planopilaris is the most common type of scarring hair loss observed, with a variety of symptoms and tissue changes.
38 citations,
January 2017 in “PPAR Research” PPAR-γ helps control skin oil glands and inflammation, and its disruption can cause hair loss diseases.
 70 citations,
February 2017 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
70 citations,
February 2017 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Treatment with plasma rich in growth factors improved hair density and thickness for hair loss patients.
 2 citations,
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology”
2 citations,
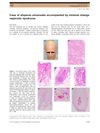
August 2015 in “Journal of dermatology” A possible link exists between minimal change nephrotic syndrome and complete hair loss.
 18 citations,
March 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
18 citations,
March 2004 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Lupus can cause hair loss and nail changes, with treatments available for both.
 September 2023 in “International journal of women’s dermatology”
September 2023 in “International journal of women’s dermatology” Certain hairstyles, diabetes, scalp infections, and vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of hair loss in Black women; more research is needed for better treatment.
 July 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
July 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Reflectance confocal microscopy helped tell periorificial dermatitis apart from similar skin conditions.
 18 citations,
November 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology”
18 citations,
November 2020 in “Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology” Inflammation plays a key role in activating skin stem cells for hair growth and wound healing, but more research is needed to understand how it directs cell behavior.
 20 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
20 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The document says that treating the root cause of hair follicle damage is crucial to prevent permanent hair loss, and treatment options vary.























