 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Skin problems are common in Bangladesh due to arsenic, prompt treatment of diabetic foot ulcers is crucial, maternal transmission causes most neonatal herpes, treatments for pediatric vasculitis are effective, the chickenpox vaccine works, more frequent UVB therapy helps psoriasis, certain jobs increase hand dermatitis risk, monoclonal antibodies treat psoriasis well, lifestyle affects psoriasis, alefacept improves psoriasis, imiquimod cream partially clears basal cell carcinoma, and iron may not help chronic hair loss.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that various treatments for skin conditions are effective, but some require further research, and certain factors like gender and lifestyle can influence disease outcomes.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Stopping certain drugs can improve skin conditions, arsenicosis affects over half of a Bangladeshi village, males are more vulnerable, and certain treatments are effective for warts, acne, and psoriasis. Smoking and drinking are linked to psoriasis in men, a cream helps with a type of skin cancer, and low iron levels don't directly cause chronic hair loss in women.
 August 2001 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
August 2001 in “Veterinary Dermatology” The meeting presented findings on effective treatments for various pet skin conditions and insights into the immune responses of dogs with atopic dermatitis.
 September 1997 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
September 1997 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Psychological factors play a significant role in developing alopecia areata.
 July 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Low testosterone levels may contribute to female pattern hair loss in men.
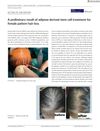 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
 165 citations,
December 2002 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
165 citations,
December 2002 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Male hormones, particularly DHT, are linked to male pattern hair loss, and treatments like finasteride can help, but they don't work for postmenopausal women's hair loss, which may have different causes.
 106 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
106 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that assessing hair follicle damage due to cyclophosphamide in mice involves analyzing structural changes and suggests a scoring system for standardized evaluation.
 99 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
99 citations,
April 2005 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Finasteride effectively treats hidradenitis suppurativa for most patients.
 98 citations,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
98 citations,
May 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” There are many treatments for permanent hair loss disorders, but their effectiveness varies and there's no clear best option.
 94 citations,
October 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
94 citations,
October 2017 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Lichen planus pigmentosus causes dark skin patches and is treated by avoiding triggers and using anti-inflammatory medications.
 82 citations,
June 2020 in “Inflammation Research”
82 citations,
June 2020 in “Inflammation Research” Skin problems in COVID-19 patients are rare and may be due to the body's complex immune response or blood clotting issues.
 64 citations,
January 2005 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
64 citations,
January 2005 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair transplant destroyed by lichen planopilaris.
 63 citations,
October 2005 in “Archives of Dermatology”
63 citations,
October 2005 in “Archives of Dermatology” Shorter, thinner hairs indicate AGA, while longer, thicker hairs suggest CTE; counting and measuring shed hairs helps diagnose hair loss type.
 56 citations,
January 2013 in “International journal of trichology”
56 citations,
January 2013 in “International journal of trichology” Zinc supplements may be needed to treat hair loss in hypothyroidism.
 47 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
47 citations,
June 2014 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Most treatments for lichen planopilaris were found to be generally unsatisfactory.
 44 citations,
May 2006 in “The Journal of the American Animal Hospital Association/Journal of the American Animal Hospital Association”
44 citations,
May 2006 in “The Journal of the American Animal Hospital Association/Journal of the American Animal Hospital Association” Both treatments for pemphigus foliaceus in dogs are effective, but combination therapy has more side effects.
 41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design”
41 citations,
February 2001 in “Current pharmaceutical design” Current and future treatments for alopecia areata focus on immunosuppression, immunomodulation, and protecting hair follicles.
 40 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of Ovarian Research”
40 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of Ovarian Research” Rutin may help treat symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in rats.
 39 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
39 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Herbs can potentially treat hair loss by inhibiting a key enzyme and promoting hair growth, and deficiencies in zinc, biotin, and iron are linked to hair loss.
 39 citations,
January 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
39 citations,
January 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Reflectance confocal microscopy confirms that yellow dots are signs of damaged hair follicles in alopecia areata.
 39 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
39 citations,
July 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Pseudopelade of Brocq is a unique hair loss condition, but its cause and development are still not fully understood.
 37 citations,
May 1999 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
37 citations,
May 1999 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for preventing permanent hair loss in various scalp conditions, and while new treatments are promising, more research is needed to evaluate their effectiveness.
 35 citations,
March 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
35 citations,
March 2014 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss in male pattern baldness involves muscle degeneration and increased scalp fat.
 33 citations,
January 2010 in “Case reports in dermatology”
33 citations,
January 2010 in “Case reports in dermatology” Dermoscopy helps diagnose frontal fibrosing alopecia by distinguishing it from other hair loss conditions.
 33 citations,
October 2004 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
33 citations,
October 2004 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Large prostate links to more hair loss, but age of onset doesn't affect it.
 32 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of neurochemistry”
32 citations,
February 2019 in “Journal of neurochemistry” Sex hormones affect brain injury differently in males and females.
 32 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a hair loss condition with acute cases resolving quickly and chronic cases potentially lasting longer, sometimes requiring treatment.
 29 citations,
April 2013 in “Mycoses”
29 citations,
April 2013 in “Mycoses” A young man was initially misdiagnosed with a scalp condition but was found to have a fungal infection, which improved with antifungal treatment.





























