1 citations,
January 2019 in “Indian journal of paediatric dermatology” Kids with alopecia areata had lower vitamin D levels than healthy kids.
 13 citations,
January 2018 in “BioMed Research International”
13 citations,
January 2018 in “BioMed Research International” Scalp involvement is common in pemphigus and can lead to hair loss, with the severity of scalp lesions linked to overall disease severity.
December 2020 in “Galen Medical Journal” Alopecia patients have more mast cells in their scalps, especially in severe cases and older age, with alopecia areata showing the highest increase.
5 citations,
January 2015 in “Case reports in medicine” A baby was diagnosed with IFAP syndrome due to a new genetic mutation, showing severe skin and developmental issues.
10 citations,
July 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology”  March 2023 in “Revista médica Clínica Las Condes”
March 2023 in “Revista médica Clínica Las Condes” The study suggests a possible increase in androgen receptors in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia, but more research is needed.
14 citations,
January 2018 in “Skin Appendage Disorders” Upper eyelid hyperpigmentation can help diagnose facial lichen planus pigmentosus in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia.
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” PEODDN is a rare skin disorder with limited treatment options, best treated with laser therapy.
September 2022 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopic measurements help determine the severity of female pattern hair loss.
A 2-year-old boy with a rare type of lupus causing hair loss improved with oral steroids.
 13 citations,
April 2022 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
13 citations,
April 2022 in “Anais brasileiros de dermatologia/Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” The document concludes that more research is needed to find effective treatments for Lichen planopilaris and Frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 November 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii”
November 2020 in “Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii” Sulfotransferase SULT1A1 activity may predict minoxidil treatment success for hair loss.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Various skin conditions like cutaneous lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, and basal cell carcinoma can be effectively treated with antihypertensive agents, NB-UVB phototherapy, and imiquimod cream respectively. Vaccines are effective against genital herpes and HPV-16 infection. Early intervention is crucial for conditions like diabetic foot ulcers and neonatal herpes. Certain dyes can cause hand dermatitis, and there's a link between smoking/drinking and psoriasis in men. No direct link was found between low iron levels and chronic hair loss in women.
 5 citations,
August 2020 in “Curēus”
5 citations,
August 2020 in “Curēus” The document concludes that recent studies help tell apart desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas from other skin tumors, but more research is needed for clear differentiation.
 15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology”
15 citations,
April 2003 in “Journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss due to an immune attack on hair follicles, influenced by genetics and environment.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Certain drugs can cause skin lupus, but stopping the drug usually helps. Vaccines work against smallpox, genital herpes, and a type of human papillomavirus. More frequent light therapy clears psoriasis faster. Certain treatments work for psoriasis and dermatitis. A specific cream effectively treats a type of skin cancer. Low iron levels aren't directly linked to chronic hair loss.
March 2022 in “International Journal of Trichology” Smoking may worsen hair loss, but more research is needed.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Certain drugs can cause lupus, stopping these drugs is the main treatment. NB-UVB phototherapy clears psoriasis faster when applied three times a week. Monoclonal antibodies and oral pimecrolimus are effective in treating psoriasis. Smoking and drinking are linked to psoriasis in men. No direct link between low iron and hair loss was found. Vaccines are effective against genital herpes and human papillomavirus type 16.
January 2020 in “Menoufia Medical Journal” IGF-1R may play a role in female hair loss and could be a treatment target.
 August 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Melanocytes may trigger the immune response in alopecia areata, affecting hair regrowth.
 1 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences”
1 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of evolution of medical and dental sciences” Older people in Kerala often have skin conditions, with dry skin being the most common, and certain skin issues are linked to high cholesterol and diabetes.
2 citations,
January 1989 in “PubMed”  15 citations,
September 2013 in “Pharmaceutical Biology”
15 citations,
September 2013 in “Pharmaceutical Biology” Jujube fruit extract may reduce kidney damage from ibuprofen in rats.
 December 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
December 2021 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” The study concluded that female pattern hair loss is linked to psychological distress and is hard to diagnose and treat, with its causes still not fully understood.
 6 citations,
April 2017 in “Experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
April 2017 in “Experimental dermatology” CD80CD86 deficiency causes hair loss by disrupting regulatory T cells.
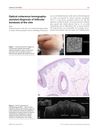 5 citations,
February 2015 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
5 citations,
February 2015 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” OCT can non-invasively diagnose follicular keratosis and other hair follicle disorders.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Blood pressure drugs can cause skin lupus, early treatment is key for baby herpes and diabetic foot ulcers, a certain vaccine works against genital herpes and HPV in women, more frequent light therapy helps psoriasis, smoking and drinking can worsen psoriasis, a cream clears up a type of skin cancer, and low iron levels don't cause chronic hair loss.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Various skin conditions can be treated effectively with different methods, such as discontinuing certain drugs, using specific vaccines, applying creams, and changing lifestyle habits like smoking and drinking.
 June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” UK medical students lack dermatology education, liver biopsy patients with risk factors show more fibrosis, and certain fungi resist drugs due to melanin; genetics may influence female hair loss.
 June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” A woman's rare hair loss condition improved on its own, suggesting this type might recover like common cases.


















