 1 citations,
January 2013 in “MedChemComm”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “MedChemComm” PF-05314882 selectively activates androgen receptors without much effect on prostate and may help in prostate cancer treatment and hair loss prevention.
 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
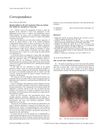
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 60 citations,
May 2015 in “Archives of dermatological research”
60 citations,
May 2015 in “Archives of dermatological research” PPAR agonists show promise for skin conditions but need more research before being a main treatment.
 19 citations,
October 2017 in “The FASEB Journal”
19 citations,
October 2017 in “The FASEB Journal” Male hormones cause different growth in identical human hair follicles due to their unique epigenetic characteristics.
25 citations,
July 1994 in “Journal of dermatological science” Testosterone affects hair follicles differently across body sites, with beard hair follicles showing more activity of a specific enzyme and presence of androgen receptors compared to scalp hair.
 157 citations,
April 1994 in “Clinical endocrinology”
157 citations,
April 1994 in “Clinical endocrinology” Androgens can cause hair growth in some areas and hair loss on the scalp.
 9 citations,
August 2014 in “European journal of ophthalmology”
9 citations,
August 2014 in “European journal of ophthalmology” PGF2α receptors in human eyelids are found in specific parts of hair follicles, explaining eyelash changes with glaucoma treatment.
 23 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation”
23 citations,
December 2004 in “Differentiation” Sex hormones affect hair and feather growth and may help manage alopecia and hormone-dependent cancers.
84 citations,
February 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology” PPARγ is crucial for skin health but can have both beneficial and harmful effects.
4 citations,
July 2006 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Testosterone increases hair follicle cell growth when beard or axillary skin cells are present together.
 28 citations,
March 2017 in “Endocrinology”
28 citations,
March 2017 in “Endocrinology” Removing vitamin D and calcium receptors in mice skin cells slows down skin wound healing.
 1 citations,
January 2022 in “BMC Genomic Data”
1 citations,
January 2022 in “BMC Genomic Data” The study found that androgen receptors in skin cells mainly affect the focal adhesion pathway and control the caveolin-1 gene, with implications for new treatments for related diseases.
 November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
November 2022 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Different types of PPARγ are found in varying amounts in human skin and its parts, which could affect how skin treatments work.
 1 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal of Biosciences and Medicines”
1 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal of Biosciences and Medicines” Understanding how androgens and their receptors work can lead to improved treatments for skin diseases.
 7 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
7 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Vitamin A may influence hair loss conditions like alopecia, but more research is needed to understand how.
31 citations,
April 2015 in “Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology/The Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology” Androgens cause oil-producing skin cells with androgen receptors to mature and produce more oil.
Sansevieria trifasciata Prain shows promise for treating hair loss by inhibiting androgen receptors.
 3 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia”
3 citations,
September 1980 in “Experientia” Dobutamine does not mimic dopamine at therapeutic doses but may at very high concentrations; microfilaments, not microtubules, are important for wound healing in Xenopus embryos.
 October 2023 in “IBRO neuroscience reports”
October 2023 in “IBRO neuroscience reports” Rat hair follicle stem cells have functional oxytocin receptors, useful for studying neuropsychiatric disorders.
 July 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual”
July 2023 in “Dermatology practical & conceptual” Women with Female Pattern Hair Loss may experience more stress, anxiety, and depression, and have lower levels of BDNF, which could predict the psychological impact.
 22 citations,
June 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
22 citations,
June 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” A woman had both Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome, causing hair loss, and complete androgen insensitivity syndrome, making her genetically male but physically female. This suggests androgens don't affect the hair loss condition.
 27 citations,
April 1998 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
27 citations,
April 1998 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” Estrogen and progesterone don't directly affect hair growth in androgenic alopecia and alopecia areata.
11 citations,
July 2012 in “Experimental dermatology” Innate immunity genes in hair follicle stem cells might have new roles beyond traditional immune functions.
 4 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Prostaglandins may contribute to male hair loss; targeting them could help treat it.
March 2023 in “Natural product sciences” Celtis choseniana may help treat hair loss by reducing androgen effects and boosting hair growth signals.
 October 2024 in “Current Issues in Molecular Biology”
October 2024 in “Current Issues in Molecular Biology” Platycladus orientalis leaf extract helps hair grow by activating certain proteins.
 291 citations,
April 2010 in “Gastroenterology”
291 citations,
April 2010 in “Gastroenterology” Certain proteins, Lgr5 and Lgr6, are important markers of adult stem cells and are involved in tissue repair and cancer development.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry”
December 2024 in “Journal of Medicinal Chemistry” A new topical treatment for hair loss shows promise by targeting androgen receptors.
 80 citations,
April 2017 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology”
80 citations,
April 2017 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” PDRN helps repair tissue and improve wound healing with a high safety profile.
January 2024 in “Neuroscience Applied” Oxytocin receptor changes in hair cells may help identify autism, especially in males.





















