 10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care”
10 citations,
June 2000 in “Primary Care” The document explains different hair loss types and treatments, emphasizing diagnosis through examination and tests, and specific treatments for each condition.
 7 citations,
February 2016 in “Dermatology and therapy”
7 citations,
February 2016 in “Dermatology and therapy” t-Flavanone helps improve male pattern hair loss by making hair roots stronger.
 4 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
4 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Pumpkin seed oil slightly outperforms minoxidil foam in treating hair loss with fewer side effects.
 4 citations,
April 2020 in “JAAD case reports”
4 citations,
April 2020 in “JAAD case reports” JAK inhibitors help hair regrowth but not fully effective for androgenetic alopecia.
 4 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
November 2009 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Stress, nutritional issues, and chronic diseases can cause hair loss, and nail changes may signal internal diseases; treatment focuses on the underlying cause.
 3 citations,
July 2021 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery”
3 citations,
July 2021 in “Aesthetic Plastic Surgery” PHAT may improve hair growth better than PRP alone.
 3 citations,
March 2016 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2016 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” GPIGS peptide increases thick hair growth in balding Japanese men.
 2 citations,
March 2021 in “Cosmetics”
2 citations,
March 2021 in “Cosmetics” Hair transplant surgery is the most effective, safe, and satisfying treatment for hair loss.
 2 citations,
June 2020 in “Skin Research and Technology”
2 citations,
June 2020 in “Skin Research and Technology” MRI reveals thinner scalps and smaller hair follicles in people with androgenetic alopecia.
 2 citations,
June 2000 in “Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery”
2 citations,
June 2000 in “Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery” Hair transplantation techniques have improved over time, leading to natural-looking results and high graft survival rates, making it a popular treatment for hair loss.
 1 citations,
January 2020 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Platelet-rich plasma and stem cell therapies are accepted treatments for hair restoration, with specific protocols recommended for best results, but more standardization is needed in stem cell use.
 1 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders”
1 citations,
January 2020 in “Skin appendage disorders” Hair transplants for male baldness can show inflammation and fibrosis, but more research is needed to confirm LPP presence.
 1 citations,
January 2001 in “Cosmetics and toiletries”
1 citations,
January 2001 in “Cosmetics and toiletries” Procyanidin B-2 from apple juice significantly increases hair growth and may be more effective than minoxidil without side effects.
 May 2024 in “Medicine today”
May 2024 in “Medicine today” Older age, family history, and low iron levels increase the risk of female hair loss.
 June 2023 in “Sains Malaysiana”
June 2023 in “Sains Malaysiana” Cinchonine Nanostructured Lipid Carriers serum safely and effectively stimulates hair growth and increases the number and size of hair follicles.
 April 2021 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery”
April 2021 in “Advances in Cosmetic Surgery” Hair restoration can be achieved through non-surgical treatments like minoxidil, antiandrogens, phototherapy, and PRP procedures, or through surgical methods like hair transplantation. Continued treatment is needed to maintain results, and full results are visible after 12-18 months.
 February 2018 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
February 2018 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Nonshaven follicular unit extraction is a highly satisfactory method for restoring pubic hair.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Gender affects hair and scalp characteristics, with differences in hormone responses, graying patterns, and trace metals.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that there are various causes and treatments for hair loss, with hair transplantation being a notable option.
 January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Some alternative treatments may help with hair loss, but more evidence is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cortexolone 17a-propionate may be an effective new treatment for hair loss.

Chrysanthemum zawadskii extract may help treat hair loss by promoting hair growth and affecting growth factors.
 May 1993 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
May 1993 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Surgical hair replacement is a viable option for male pattern baldness when done with proper planning and realistic expectations.
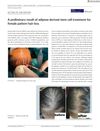 April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Stem cell treatment improved hair density in female hair loss patient.
 February 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
February 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Injections improve hair growth, density, and thickness in women safely.
 88 citations,
June 2009 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine”
88 citations,
June 2009 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” To manage diffuse hair loss, identify the cause, improve nutrition, remove triggers, and use specific treatments like minoxidil or finasteride.
 76 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
76 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Japanese women typically start experiencing hair loss after 40, with reduced hair density and thickness being the main factors.
 70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery”
70 citations,
February 2015 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery” Topical drugs and near-infrared light therapy show potential for treating alopecia.
 59 citations,
May 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets”
59 citations,
May 2014 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Targets” The document concludes that targeting 5α-reductase, the androgen receptor, and hair growth genes, along with using compounds with anti-androgenic properties, could lead to more effective hair loss treatments.
 59 citations,
August 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
59 citations,
August 1998 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Genetics and hormones cause hair loss; finasteride treats it safely.






























