 May 2023 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology”
May 2023 in “Journal of Ethnopharmacology” The wild garlic plant, Allium macrostemon Bunge, can promote hair growth and could potentially be used to treat hair loss.

The treatment was ineffective in humans.
ILC1-like cells may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata.
 February 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
February 2023 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Blocking IL-17 can reduce skin inflammation in a mouse model of pityriasis rubra pilaris.
ILC1-like cells can independently cause alopecia areata by affecting hair follicles.
ILC1-like cells may contribute to hair loss in alopecia areata and could be new treatment targets.
 September 2022 in “Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology”
September 2022 in “Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology” Taxifolin from Rhododendron mucronulatum may help prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
 June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
June 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” ILC1-like cells can cause alopecia areata by attacking hair follicles.

Wild African goats have genetic adaptations for surviving harsh desert conditions.
 October 2023 in “Bioactive Materials”
October 2023 in “Bioactive Materials” The new hair loss treatment combining nitric oxide and minoxidil in a special carrier is effective for hair regrowth.
 29 citations,
January 2014 in “Frontiers in physiology”
29 citations,
January 2014 in “Frontiers in physiology” Understanding and tracking our body's natural daily rhythms could help improve heart health.
44 citations,
February 2023 in “Cell” Fingerprints form uniquely before birth due to specific genetic pathways and local signals.
35 citations,
November 2021 in “Journal of nanobiotechnology” Thymol-loaded nanoparticles are a promising, natural treatment for acne that avoids antibiotics and preserves healthy skin bacteria.
 1 citations,
September 2023 in “Molecules (Basel. Online)”
1 citations,
September 2023 in “Molecules (Basel. Online)” Plant sterols have health benefits like lowering cholesterol, but more research is needed to understand their effects and improve their extraction and sustainability.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “Science Advances”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “Science Advances” High levels of ERK activity are key for tissue regeneration in spiny mice, and activating ERK can potentially redirect scar-forming healing towards regenerative healing in mammals.
 January 2024 in “Tropical journal of pharmaceutical research”
January 2024 in “Tropical journal of pharmaceutical research” Cirsium japonicum var. spinossimum seeds may help reduce inflammation and fight cancer.
22 citations,
December 2015 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” A mouse gene mutation increases the risk of skin cancer.
21 citations,
December 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” T-cells in alopecia areata scalp show abnormal regulation, leading to less inflammation.
4 citations,
February 2023 in “Frontiers in Oncology” Nano-Pulse Stimulation™ Therapy is more effective and less damaging than cryoablation for treating melanoma tumors in mice.
 28 citations,
February 1999 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
28 citations,
February 1999 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Finasteride potentially treats hair loss by reducing DHT production.
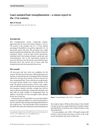 11 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Lasers in hair transplantation show promise but are not yet standard, with current methods causing some side effects and needles still being preferred for creating recipient sites.
 81 citations,
February 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
81 citations,
February 1997 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Minoxidil boosts hair growth by activating PGHS-1.
 47 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
47 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Hair diversity is influenced by complex genetics and environmental factors, requiring more research for practical solutions.
 16 citations,
October 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
16 citations,
October 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy can cause significant hair thinning and changes in hair texture, while tamoxifen has a smaller effect.
 15 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
15 citations,
May 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Low-level laser treatment helps mice grow hair by increasing certain protein levels linked to hair growth.
 13 citations,
January 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports”
13 citations,
January 2022 in “Stem cell reviews and reports” Mouse stem cells from hair follicles can improve wound healing and reduce scarring.
 12 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
12 citations,
August 2013 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Choose hair restoration surgery candidates carefully and plan treatments for a natural look and future hair loss.
 4 citations,
March 2015 in “Skin Research and Technology”
4 citations,
March 2015 in “Skin Research and Technology” Trichotillometry is a reliable method to measure hair strength and assess hair loss treatments.

Human scalp hair follicles have PGE2 and its receptors, which might affect hair growth.
 162 citations,
August 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
162 citations,
August 2005 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The new "differential stripping" method effectively measures how much substance gets into hair follicles.





















